Ingest cloud resources with Datadog
This guide aims to show you how to ingest cloud resources using Datadog to have a good grasp of the cloud resources/entities you have from your cloud provider.
Common use cases
- Map your monitored resources from cloud providers in Datadog
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have a Port account and that you have finished the onboarding process.
- You have installed and setup Port's Datadog integration
- You have installed integrations for GCP, AWS and Azure on your Datadog environment
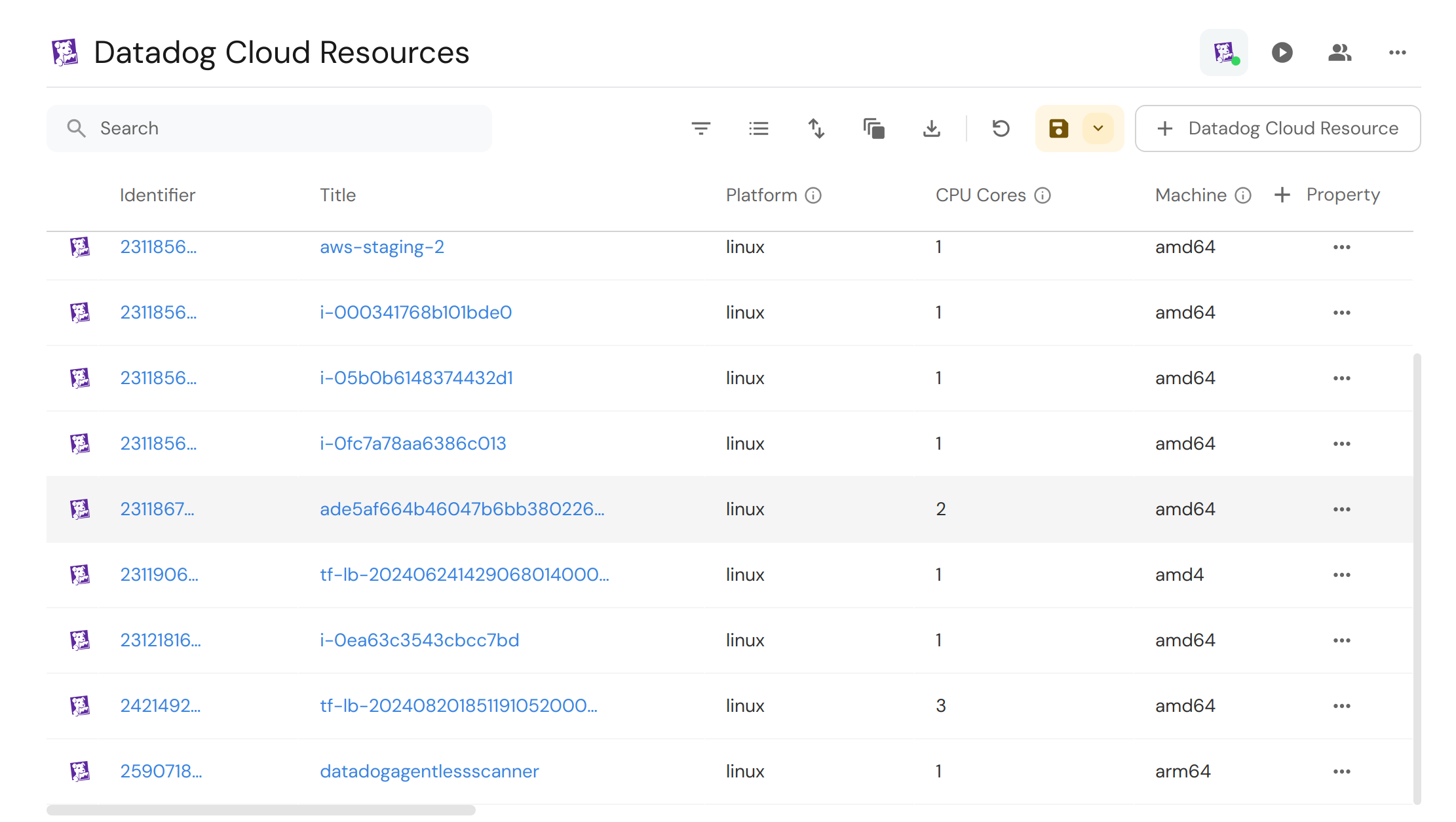
Ingesting cloud resources into Port
We will be making use of the hosts kind in Port's Datadog integration which provides information on hosts existing on the cloud providers we have configured. For this example, we are only interested in hosts with gcp, aws, and azure in the sources property.
- Having installed the Datadog integration, create the
datadogCloudResourceblueprint in your Port environment using the blueprint below:
Datadog Cloud Resource Blueprint (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "datadogCloudResource",
"description": "This blueprint represents a cloud resource in Datadog",
"title": "Datadog Cloud Resource",
"icon": "Datadog",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"up": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Is Running?",
"description": "Is the host up?"
},
"host_name": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Host Name",
"description": "the name of the host"
},
"description": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Description",
"description": "the host description"
},
"platform": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Platform",
"description": "the host platform"
},
"machine": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Machine",
"description": "The CPU architecture of the host machine (e.g., amd64, x86, x64, arm, arm64)."
},
"cpu_cores": {
"type": "number",
"title": "CPU Cores",
"description": "the host CPU cores"
},
"agent_version": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Datadog Agent Version",
"description": "the Datadog agent version installed on the host"
},
"is_muted": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Is Host Muted?",
"description": "Indicates whether alerts for that specific host are temporarily suppressed."
},
"sources": {
"title": "Sources",
"type": "array",
"description": "Source or cloud provider associated with your host."
},
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "object",
"description": "Tags associated with the host."
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
-
Head over to the Data Sources page in your Port environment and select the Datadog integration
-
Create a new mapping config with the following
Datadog Cloud Resource mapping config (Click to expand)
deleteDependentEntities: true
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
resources:
- kind: host
selector:
query: >-
[.sources[] | . as $source | ["azure", "gcp", "gce", "aws"] |
contains([$source])] | any(.)
port:
entity:
mappings:
blueprint: '"datadogCloudResource"'
identifier: .id | tostring
title: .aws_name // .host_name
properties:
up: .up
host_name: .host_name
platform: .meta.platform
is_muted: .is_muted
machine: .meta.machine
description: .description
sources: .sources
cpu_cores: .meta.cpuCores
agent_version: .meta.agent_version
tags: .tags_by_source
Cloud resources from Datadog are hosts from the host kind of the Datadog integration which are from GCP, AWS or Azure. To ingest them, we have to specify a selector which allows only such hosts with the sources we specify.
By doing this, we are able to ingest all cloud resources from Datadog
- Finally, click
resync. Your cloud resources from Datadog should now be ingested: