Ingest dependencies from a package.json file and relate them to service
This guide will demonstrate how to ingest dependencies from a package.json file and relate them to the corresponding service entities in Port.
- Ensure you have a Port account and have completed the onboarding process.
- The
Serviceblueprint should be created during the onboarding process. - Ensure you have GitHub installed and configured in your environment.
Add the Dependency blueprint if it doesn't exist:
- Go to the Builder in your Port portal.
- Click on "+ Blueprint".
- Click on the
{...}button in the top right corner, and choose "Edit JSON" - Add this JSON schema:
Dependency blueprint (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "dependency",
"title": "Dependency",
"icon": "Package",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"package_name": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "string",
"title": "Package name"
},
"semver_requirement": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Semver requirement"
},
"type": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Type",
"enum": [
"Production",
"Development"
]
},
"url": {
"type": "string",
"title": "URL",
"format": "url"
}
},
"required": [
"package_name",
"semver_requirement"
]
}
}
How to ingest dependencies from a package.json file
To ingest dependencies listed in package.json files, follow these steps:
- Go to the data sources page in your Port portal, and select your GitHub integration.
- Modify the mapping to include the
filekind with the configuration provided below:
Port Configuration (Click to expand)
- kind: file
selector:
query: 'true'
files:
- path: '**/package.json'
port:
itemsToParse: .file.content.dependencies | to_entries
entity:
mappings:
identifier: >-
.item.key + "_" + (.item.value | gsub("\\^"; "caret_") |
gsub("~"; "tilde_") | gsub(">="; "gte_") | gsub("<="; "lte_") |
gsub(">"; "gt_") | gsub("<"; "lt_") | gsub("@"; "at_") |
gsub("\\*"; "star") | gsub(" "; "_"))
title: .item.key + "@" + .item.value
blueprint: '"dependency"'
properties:
package_name: .item.key
semver_requirement: .item.value
kind: filespecifies that the source is a file, in this case,package.json.files:defines the path pattern to locatepackage.jsonfiles within your repositories.itemsToParse:identifies the specific array within thepackage.json(i.e.,dependencies) that you want to parse into individualdependencyentities.identifier:constructs a unique identifier for each dependency, accounting for special characters in the version string.properties:captures essential details like the package name and version.
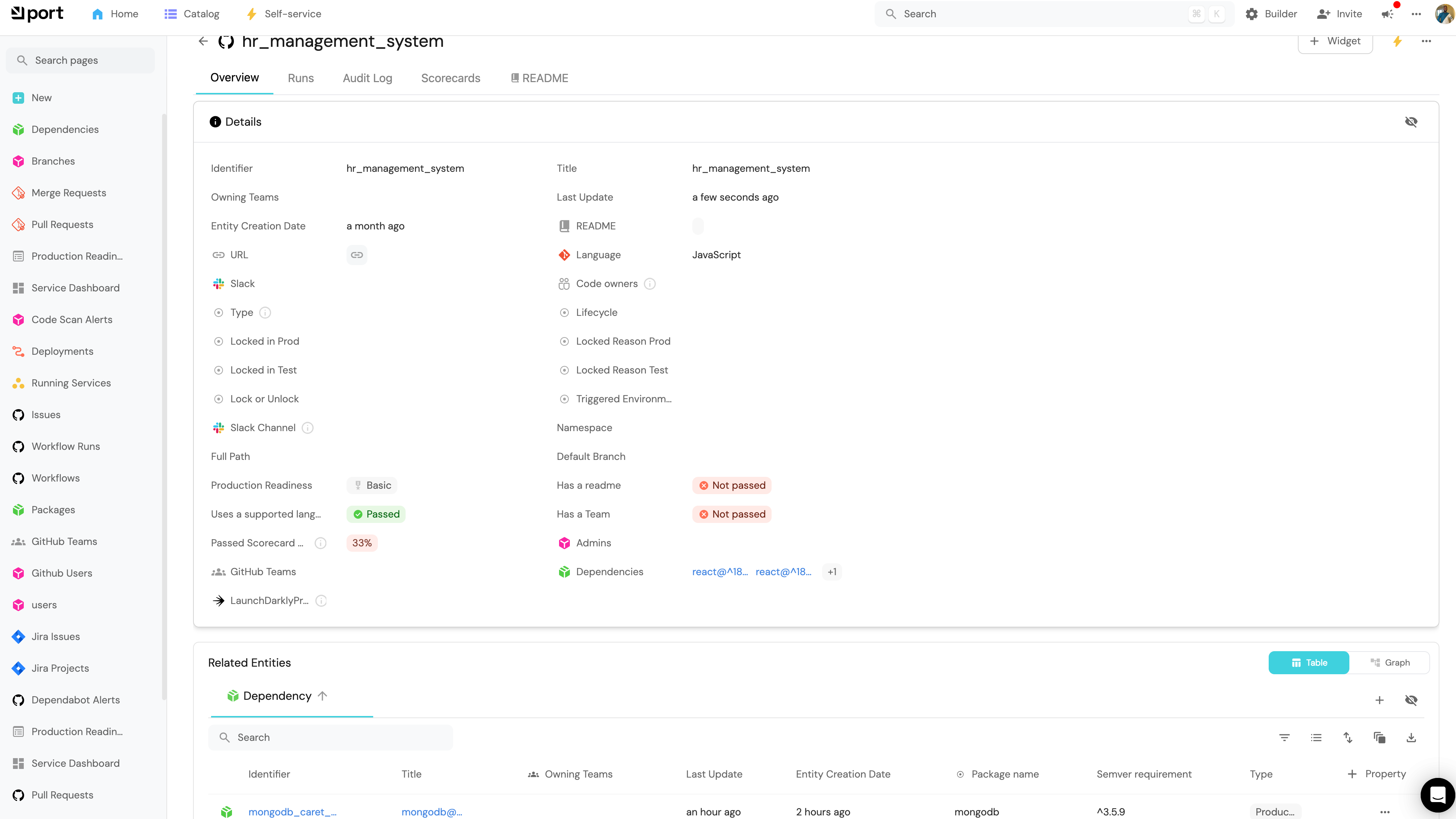
How to Relate the Dependencies to the Service
Once the dependencies have been ingested, the next step is to establish relationships between these dependency entities and the corresponding service entities.
-
Go to the Builder in your Port portal, select the
Serviceblueprint, and click onNew relationto create a relation between theserviceanddependencyblueprints. -
Add this JSON to establish the relationship:
{
"dependencies": {
"title": "Dependencies",
"target": "dependency",
"required": false,
"many": true
}
} -
Head back to the data sources page and add the mapping below:
Relation Mapping (Click to expand)
- kind: file
selector:
query: 'true'
files:
- path: '**/package.json'
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .repo.name
blueprint: '"service"'
properties: {}
relations:
dependencies: >-
[.file.content.dependencies | to_entries | map( .key + "_" +
(.value |
gsub("\\^"; "caret_") |
gsub("~"; "tilde_") |
gsub(">="; "gte_") |
gsub("<="; "lte_") |
gsub(">"; "gt_") |
gsub("<"; "lt_") |
gsub("@"; "at_") |
gsub("\\*"; "star") |
gsub(" "; "_")
) ) | .[]]
This would establish a relation between the service and dependency entities based on the dependencies listed in the package.json file.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can effectively ingest dependencies from package.json files and relate them to the corresponding service entities in Port 🎉.
More relevant guides and examples: