Promote Deployment to Production
In this guide, we will create a self-service action in Port that executes a GitHub workflow to promote an image from staging to production.
- Self-service: Enable developers to update production environments through GitOps.
- Traceability: Track the source of the image and the user that triggered the action.
This workflow automates updating your production deployment manifests with new staging container images. It then opens (and optionally merges) GitHub pull requests, enabling your GitOps operator to seamlessly redeploy the service.
Prerequisites
- Install Port's GitHub app by clicking here. This will automatically sync all your selected repositories into Port.
- A repository to contain your ArgoCD deployment manifests and action resources i.e. the github workflow file. This repository would usually be your infrastructure repositiry containing the manifests for all the apps in the different environments.
- Create the following GitHub Action secrets:
PORT_CLIENT_ID- Port Client ID learn morePORT_CLIENT_SECRET- Port Client Secret learn moreMY_GITHUB_TOKEN- a Classic Personal Access Token with thereposcope and the following permissions:pull_requests:write(to create PR) andcontents:write(to merge PR)
Port Configuration
Blueprints
Create the following blueprints in your Port account. These will model an application and its deployments across environments:
Service: Defines your GitOps application.Running Service: Represents a running instance of your application in a specific environment (e.g., dev, test, production).Image: Tracks the container image used within aRunning Service.
If you do not have the images ingested already, we recommend using our AWS ECR script, Google Container Registry script, JFrog build script or GitHub packages script to sync data to your catalog
For each of the blueprints:
-
Head to the Builder page.
-
Click on the
+ Blueprintbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the blueprint's JSON configuration into the editor.
Service blueprint (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "service",
"title": "Service",
"icon": "Github",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"readme": {
"title": "README",
"type": "string",
"format": "markdown",
"icon": "Book"
},
"url": {
"title": "URL",
"format": "url",
"type": "string",
"icon": "Link"
},
"language": {
"icon": "Git",
"type": "string",
"title": "Language",
"enum": ["GO", "Python", "Node", "React"],
"enumColors": {
"GO": "red",
"Python": "green",
"Node": "blue",
"React": "yellow"
}
},
"slack": {
"icon": "Slack",
"type": "string",
"title": "Slack",
"format": "url"
},
"code_owners": {
"title": "Code owners",
"description": "This service's code owners",
"type": "string",
"icon": "TwoUsers"
},
"type": {
"title": "Type",
"description": "This service's type",
"type": "string",
"enum": ["Backend", "Frontend", "Library"],
"enumColors": {
"Backend": "purple",
"Frontend": "pink",
"Library": "green"
},
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"lifecycle": {
"title": "Lifecycle",
"type": "string",
"enum": ["Production", "Experimental", "Deprecated"],
"enumColors": {
"Production": "green",
"Experimental": "yellow",
"Deprecated": "red"
},
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"locked_in_prod": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"title": "Locked in Prod",
"type": "boolean",
"default": false
},
"locked_reason_prod": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"title": "Locked Reason Prod",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Image blueprint (click to expand)
{
"identifier": "image",
"description": "This blueprint represents an image",
"title": "Image",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"registryId": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Registry ID",
"description": "The ID of the registry",
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"digest": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Image Digest",
"description": "SHA256 digest of image manifest",
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Image Tags",
"description": "List of tags for the image",
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"pushedAt": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Pushed At",
"description": "Date and time the image was pushed to the repository",
"format": "date-time",
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"lastRecordedPullTime": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Last Recorded Pull Time",
"description": "Date and time the image was last pulled",
"format": "date-time",
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"triggeredBy": {
"type": "string",
"icon": "TwoUsers",
"title": "Triggered By",
"description": "The user who triggered the run"
},
"commitHash": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Commit Hash",
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"pullRequestId": {
"type": "string",
"icon": "Git",
"title": "Pull Request ID"
},
"workflowId": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Workflow ID",
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
},
"image_branch": {
"title": "Image branch",
"type": "string",
"description": "The git branch associated with the repository used to build the Image"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Running Service blueprint (click to expand)
The gitPath directs the GitHub workflow to the location of your application's manifests inside your Git repository. This is so that the workflow can update the image. For instance:
- Service:
messenger - Running Service:
messenger_prod - Manifest File:
deployment.yml
A possible gitPath could be: apps/messenger/prod/deployment.yml
{
"identifier": "running_service",
"description": "This blueprint represents an ArgoCD Application",
"title": "Running Service",
"icon": "Argo",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"pullRequest": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Merged PR",
"icon": "Github",
"default": "https://github.com"
},
"locked": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Locked",
"description": "Indicate if deploying is allow for microservice in a this environment",
"default": false
},
"gitPath": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Path",
"description": "The path within the Git repository where the application manifests are located"
},
"destinationServer": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Destination Server",
"format": "url"
},
"syncStatus": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Sync Status",
"enum": [
"Synced",
"OutOfSync",
"Unknown"
],
"enumColors": {
"Synced": "green",
"OutOfSync": "red",
"Unknown": "lightGray"
},
"description": "The sync status of the application"
},
"healthStatus": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Health Status",
"enum": [
"Healthy",
"Missing",
"Suspended",
"Degraded",
"Progressing",
"Unknown"
],
"enumColors": {
"Healthy": "green",
"Missing": "yellow",
"Suspended": "purple",
"Degraded": "red",
"Progressing": "blue",
"Unknown": "lightGray"
},
"description": "The health status of the application"
},
"createdAt": {
"title": "Created At",
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
},
"grafana_link": {
"title": "Grafana Link",
"icon": "Grafana",
"type": "string",
"format": "url"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {
"service_name": {
"path": "service.$title"
}
},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"image": {
"title": "Image Deployed",
"target": "image",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"service": {
"title": "Service",
"target": "service",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
}
Port Action
-
Head to the self-service page page.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} EditJSON button. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Port Action: Promote Deployment
Make sure to replace <GITHUB_ORG> and <GITHUB_REPO> with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.
{
"identifier": "promote_image",
"title": "Promote Image",
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"description": "Promote an image to another running service",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"production_runtime": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Production Runtime",
"blueprint": "running_service",
"description": "The production runtime",
"format": "entity"
},
"auto_merge_pr": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Auto Merge PR",
"description": "Automatically merge the created PR",
"default": false
}
},
"required": [
"production_runtime",
"auto_merge_pr"
],
"order": [
"production_runtime"
]
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "running_service"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO-NAME>",
"workflow": "promote-production.yml",
"workflowInputs": {
"production_runtime": "{{ .inputs.production_runtime }}",
"auto_merge_pr": "{{ .inputs.auto_merge_pr }}",
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"port_payload": {
"trigger": "{{ .trigger }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}",
"blueprint": "{{ .action.blueprint }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
}
- Click
Save.
Now you should see the Promote to Production action in the self-service page. 🎉
Github Workflow
Create a workflow file under .github/workflows/promote-production.yml with the following content.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for your GitOps application manifests.
GitHub workflow script
<IMAGE_PROPERTTY_PATH>This guide assumes a standard image path of .spec.template.spec.containers[0].image for your application manifests. If your image path differs, you may need to adjust the workflow accordingly.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: messenger
spec:
replicas: 2
revisionHistoryLimit: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: messenger
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: messenger
spec:
containers:
- image: messenger_v2
name: messenger
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
limits:
cpu: "0.5"
memory: "512Mi"
name: Promote Production
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
entity:
description: "The running service entity"
required: true
default: "service"
production_runtime:
description: "The production running service entity"
required: true
auto_merge_pr:
description: "Auto merge the pull request"
required: false
default: "false"
port_payload:
required: true
description: >-
Port's payload, including details for who triggered the action and
general context (blueprint, run id, etc...)
env:
auto_merge: ${{ inputs.auto_merge_pr }}
jobs:
promote-deployment:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Inform execution of request to promote deployment image
id: promote
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
logMessage: "About to promote deployment image from staging to production..."
- name: Get the Staging Image
id: get-staging-image
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: GET
blueprint: image
identifier: ${{ fromJson(inputs.entity).relations.image }}
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
logMessage: "Getting the current staging image..."
- name: Set the production running service image version
id: set-production
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: UPSERT
identifier: ${{ fromJson(inputs.production_runtime).identifier }}
blueprint: running_service
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
logMessage: "Updating the production image..."
relations: |
{
"image": "${{ fromJson(inputs.entity).relations.image }}"
}
- name: Inform Port about pull request creation status - Success
if: steps.set-production.outcome == 'success'
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
logMessage: |
Opening a pull request to update the production image
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Change the production image in the manifest file
if: steps.set-production.outcome == 'success'
id: make-changes
env:
IMAGE_PROPERTY_PATH: ".spec.template.spec.containers[0].image"
run: |
# Update the manifest file to the production image version.
manifest_file=${{ fromJson(inputs.production_runtime).properties.gitPath }}
yq -i eval '${{ env.IMAGE_PROPERTY_PATH }} = "${{ fromJson(steps.get-staging-image.outputs.entity).title }}"' $manifest_file
- name: Create Pull Request
id: create-pr
uses: peter-evans/create-pull-request@v6
with:
token: ${{ secrets.GH_TOKEN }}
commit-message: Update ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).payload.entity.title }} production image to latest staging image
committer: github-actions[bot] <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
author: ${{ github.actor }} <${{ github.actor_id }}+${{ github.actor }}@users.noreply.github.com>
signoff: false
branch: deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
title: "[Promotion] Update production image for ${{ fromJson(inputs.entity).relations.service }} to latest staging image"
body: |
Update report
- **Service**: ${{ fromJson(inputs.entity).relations.service }}
- **Production Runtime**: ${{ fromJson(inputs.production_runtime).title }}
- **Staging Image Used**: ${{ fromJson(inputs.entity).relations.image }}
- **Manifest File Path**: ${{ fromJson(inputs.production_runtime).properties.gitPath }}
- Auto-generated by [port-actions][1]
[1]: https://app.getport.io/organization/run?runId=${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
labels: |
deployment
automated pr
assignees: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).trigger.by.user.email }}
- name: Inform Port about pull request creation status - Success
if: steps.create-pr.outputs.pull-request-url != ''
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
logMessage: |
A pull request has been opened to update the production image: ${{ steps.create-pr.outputs.pull-request-url }}
- name: Merge Pull Request
if: ${{ env.auto_merge == 'true' && steps.create-pr.outcome == 'success' }}
env:
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GH_TOKEN }}
PR_URL: ${{ steps.create-pr.outputs.pull-request-number }}
pr_number: ${{ steps.create-pr.outputs.pull-request-number }}
run: |
echo "Merging pull request.. $PR_URL"
HTTP_STATUS=$(curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" \
-X PUT \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $GH_TOKEN" \
"https://api.github.com/repos/${{ github.repository }}/pulls/$pr_number/merge")
echo "HTTP Status: $HTTP_STATUS"
if [ $HTTP_STATUS -eq 200 ]; then
echo "Pull request merged successfully."
echo "merge_status=successful" >> $GITHUB_ENV
else
echo "Failed to merge PR. HTTP Status: $HTTP_STATUS"
echo "merge_status=unsuccessful" >> $GITHUB_ENV
fi
- name: Inform completion of Argocd rollback into Port
if: ${{ env.auto_merge == 'true' }}
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(github.event.inputs.port_payload).runId}}
logMessage: "Pull request merge was ${{ env.merge_status }}"
- name: Inform Port about pull request creation status - Failure
if: steps.create-pr.outputs.pull-request-url == ''
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: "FAILURE"
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId }}
logMessage: |
The promotion of the image to production failed.
- name: Inform Port about action completion
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
status: "SUCCESS"
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_payload).runId}}
logMessage: Completed promotion of deployment image from staging to production
Let's test it!
- On the self-service page, go to the
Promote to Productionaction and fill in the properties. - Click the execute button to trigger the GitHub workflow.
- You should see the following happen:
- The production
Running Serviceentity in Port is updated to the staging image. - Your production deployment manifest is updated with the staging image in GitHub.
- A pull request is created to merge this change.
- Optional: If auto-merge is enabled, the pull request will be merged automatically.
- The production
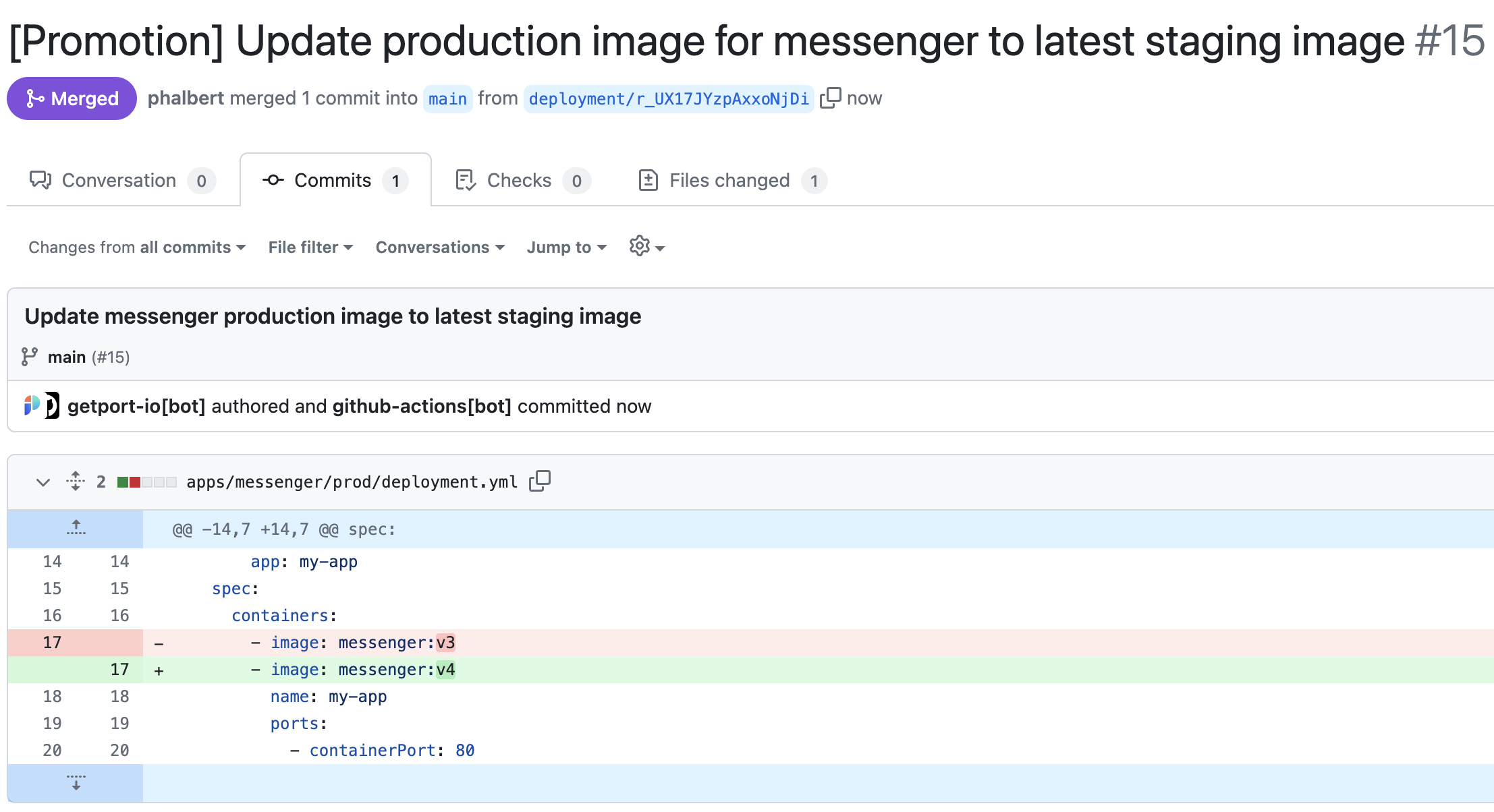
Done! 🎉 You can now promote images from staging to production.