Webhook
Overview
The webhook backend allows you to trigger your own custom webhooks, for both self-service actions and automations.
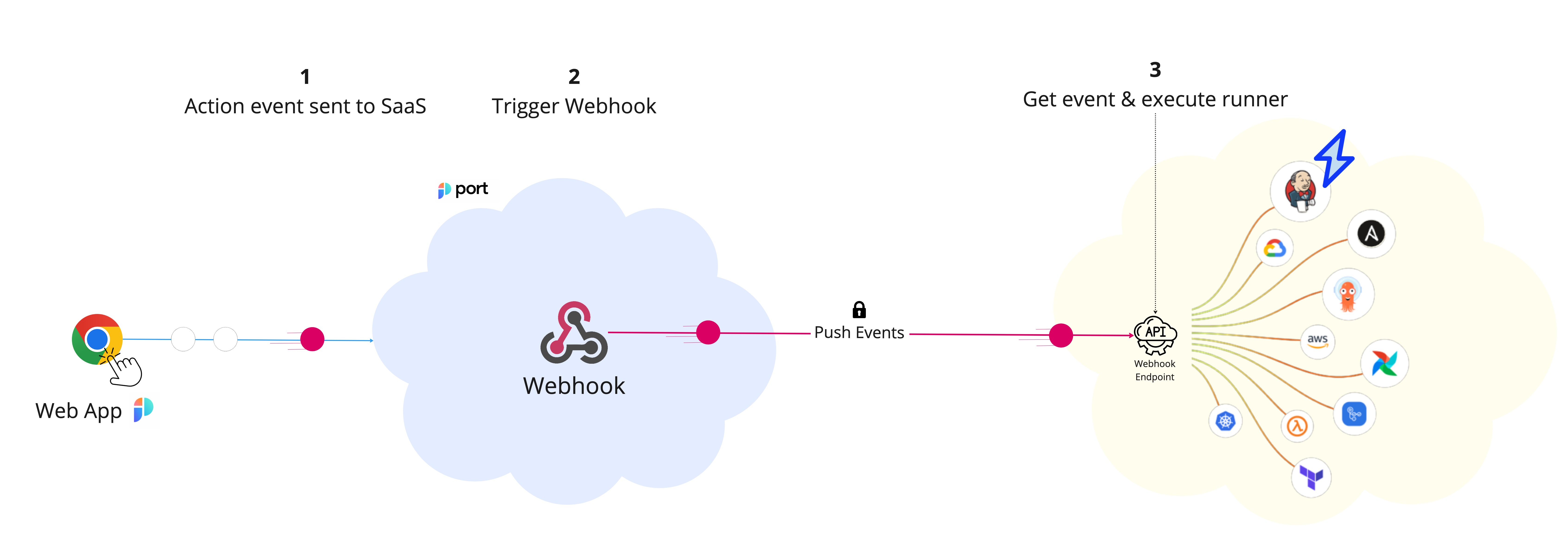
The steps shown in the image above are as follows:
-
Port generates an invocation of an action/automation.
-
Port signs the payload + timestamp using
HMAC-SHA-256and puts it in the request header.WEBHOOK SECURITYVerifying the webhook request using the request headers provides the following benefits:
-
Ensures that the request payload has not been tampered with.
-
Ensures that the sender of the message is Port.
-
Ensures that the received message is not a replay of an older message.
To learn how to verify the webhook request, refer to the Verifying Webhook Signature page.
-
-
Port publishes an invoked action/automation via a
POSTrequest to the customer definedURL. -
A listener implemented on the Client side receives the
POSTrequest and runs custom logic provided by the user.
The listener can be anything that can read from a Kafka topic and run code based on the received message, for example:
- AWS Lambda.
- Python code that reads from the topic.
- Docker container running code.
You control how you interact with webhooks, in the way that best suits your organization and infrastructure.
An example flow would be:
- A developer asks to deploy a new version of an existing
Microservice. - The
createaction is sent to the definedURL. - An AWS Lambda function is triggered by this new action message.
- The Lambda function deploys a new version of the service.
- When the Lambda is done, it reports back to Port about the new Microservice
Deployment.
Configuration
When using this backend, there are several configurations that you can customize:
Use Port agent
The Port execution agent provides you with a secure and convenient way to act upon webhook invocations of self-service actions and automations.
The agent pulls the new invocation event from your dedicated Kafka topic, and sends it to the URL you specified.
If you prefer to send a webhook without using the agent, you can validate the webhook signature for increased security.
To use the agent, set the agent field to true in the invocationMethod object, or set the Use self-hosted agent toggle to Yes if using the UI.
Request type - sync vs. async
By default, the action will be executed asynchronous, meaning that your backend will need to explicitly send Port its result via the API.
Alternatively, you can set the execution type to synchronous, which will cause the action to automatically report its result back to Port via the returned HTTP status code and payload.
HTTP method
By default, a POST request will be sent to the specified endpoint URL.
You can change the request to any of the supported types: POST, PUT, DELETE, or PATCH.
Next steps
To get started with webhook actions, check out the sources below: