Azure pipeline
The Azure backend can trigger Azure pipelines for both self-service actions and automations, using incoming webhook triggers.
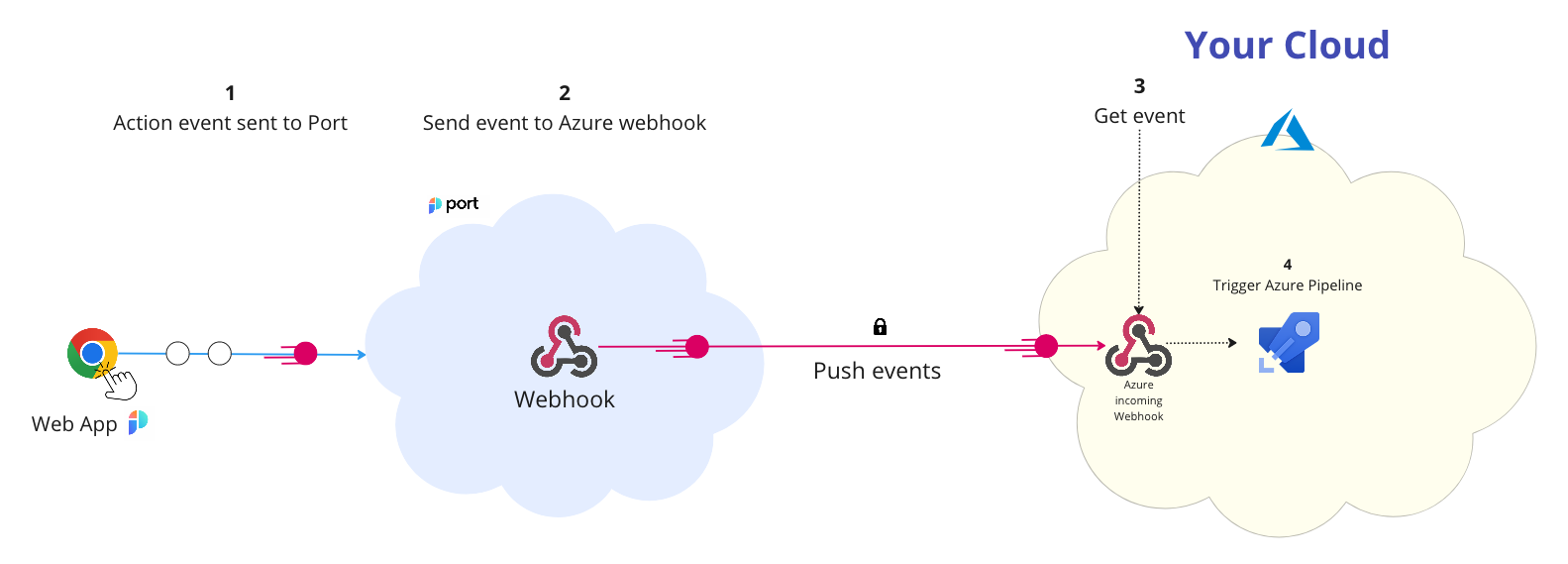
The steps shown in the image above are as follows:
-
A self-service action or automation is invoked in Port.
-
Port signs the action payload using SHA-1 with your Port
clientSecretvalue and puts it in theX-Port-Signaturerequest header.Webhook securityVerifying the webhook request using the request headers provides the following benefits:
- Ensures that the request payload has not been tampered with.
- Ensures that the sender of the message is Port.
- Ensures that the received message is not a replay of an older message.
-
Port publishes an invoked
WEBHOOKvia aPOSTrequest tohttps://dev.azure.com/{org_name}/_apis/public/distributedtask/webhooks/{webhook_name}?api-version=6.0-preview
An example flow would be:
- A developer asks to run an Azure pipeline, using a self-service action.
- Port sends a
POSTrequest with the action payload to the Azure webhookURL. - The Azure webhook receives the new action request.
- The Azure webhook triggers the pipeline.
Define Incoming Webhook in Azure
To define an incoming webhook in Azure, follow the steps below:
-
Create the Service Connection
- In your Azure DevOps project, go to Project Settings.
- Under Pipelines, click on Service connections.
- Click the Create service connection button.
- Choose Incoming WebHook as the type.
- Fill in the following fields:
- Webhook Name: The webhook name e.g. "port_trigger"
- Service connection name: The name of the service connection (e.g., "port_trigger").
- Secret key: Enter your Port
clientSecretvalue. - Headers: Type in
X-Port-Signature.
- Check
Grant access to all pipelines - Click
Save.
-
Use the Webhook in Your Pipeline
- Add the service connection resources in the Azure pipeline yaml:
The complete documentation showing how to configure Azure incoming webhooks can be found here.
resources:
webhooks:
- webhook: { webhookName }
connection: { Service connection name }
- Add the service connection resources in the Azure pipeline yaml:
Configuration
When using this backend, you need to provide the following:
- ADO organization name - can be found in your URL:
https://dev.azure.com/{AZURE-DEVOPS-ORG}. - Webhook name - the name you gave to the webhook resource in the Azure yaml pipeline file.
Examples
For complete examples of self-service actions using Azure pipelines as the backend, check out the guides section.