Triggering Cloud Build using webhooks
In this guide, you will learn how to trigger your Cloud Build Pipelines from Port, using Webhook Actions.
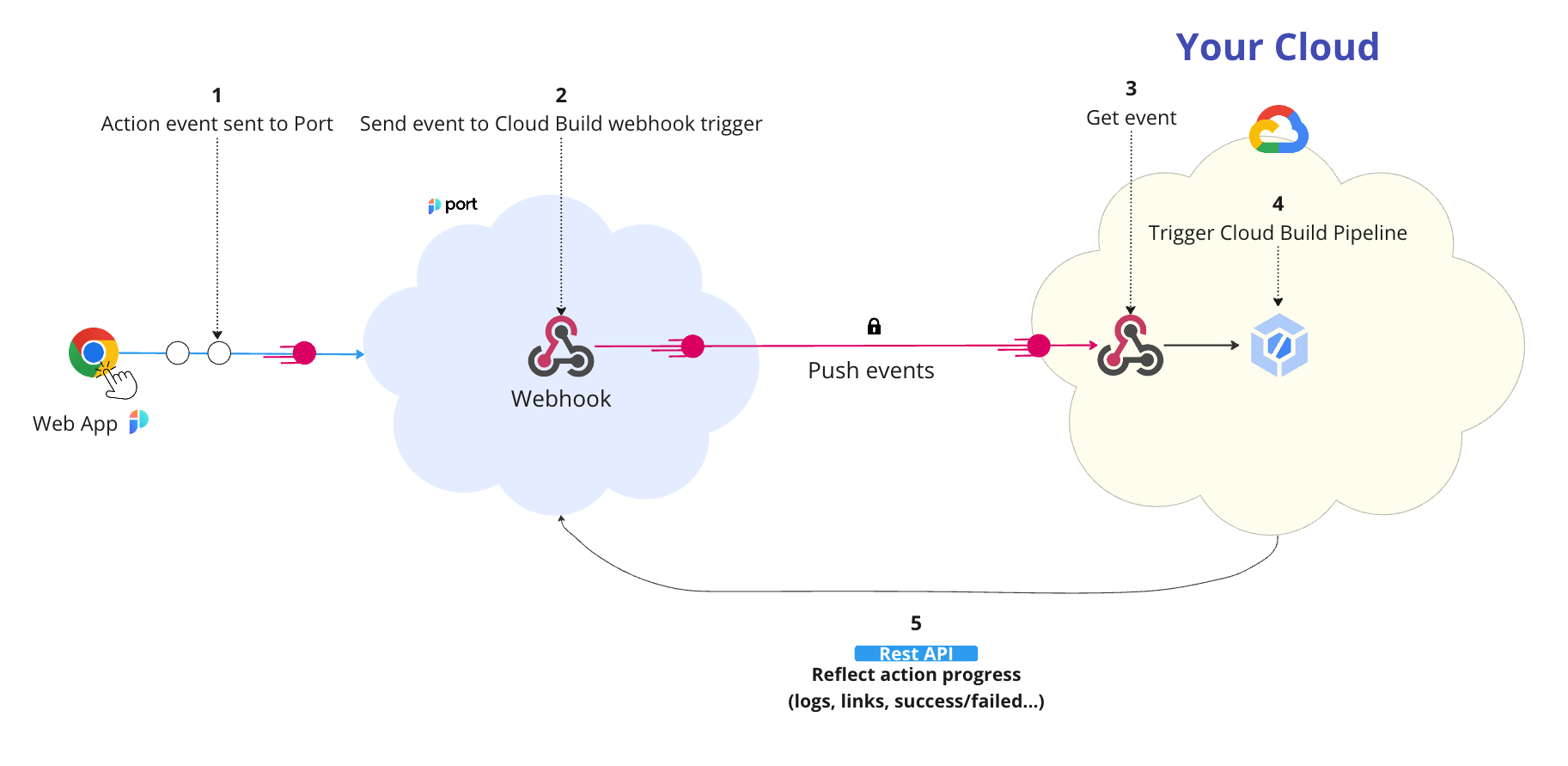
The steps shown in the image above are as follows:
-
An action is invoked in Port;
-
Port signs the action payload using SHA-1 with the
clientSecretvalue and puts it in theX-Port-Signaturerequest header.WEBHOOK SECURITYVerifying the webhook request using the request headers provides the following benefits:
- Ensures that the request payload has not been tampered with
- Ensures that the sender of the message is Port
- Ensures that the received message is not a replay of an older message
-
Port publishes an invoked
WEBHOOKvia aPOSTrequest tohttps://cloudbuild.googleapis.com/v1/projects/{project_id}/triggers/{webhook_name}:webhook?key={google_api_key}&secret={webhook_secret}
An example flow would be:
- A developer asks to run a Cloud Build pipeline;
- Port sends a
POSTrequest with the action payload to the Cloud Build webhookURL; - The Cloud Build webhook receives the new action request;
- The Cloud Build webhook triggers the pipeline;
Prerequisites
Google Cloud Build required dependencies:
- Source Code Repository - You will be asked to authorize the Google Cloud Build service to access your GitHub, Gitlab or BitBucket account to proceed.
- GCP Services - You will need to enable the following GCP APIs if you are following this tutorial:
- Cloud Run;
- Cloud Build;
- Secret Manager;
- Artifact Registry.
Setting up the webhook
Configuring the pipeline
To enable triggering a Cloud Build pipeline using a webhook invocation, you will need to add a cloudbuild.yaml file or a Dockerfile to your source code repository's root directory. This enables Cloud Build to read the pipeline steps and execute the instructions.
The following example illustrates a simple Cloud Build pipeline that builds a container image, pushes the image to container registry and deploys it using Google Cloud Run. Copy and paste this code block into your cloudbuild.yaml file.
steps:
# Build the container image
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker"
args:
[
"build",
"-t",
"${_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/${_REPOSITORY}/${_IMAGE_NAME}:${SHORT_SHA}",
".",
]
id: Building the container image
# Push the container image to Container Registry
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker"
args:
[
"push",
"${_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/${_REPOSITORY}/${_IMAGE_NAME}:${SHORT_SHA}",
]
id: Pushing the image to registry
# Deploy container image to Cloud Run
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud"
args:
[
"run",
"deploy",
"${_REPOSITORY}",
"--image",
"${_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/${_REPOSITORY}/${_IMAGE_NAME}:${SHORT_SHA}",
"--region",
"${_REGION}",
"--platform",
"managed",
"--allow-unauthenticated",
]
substitutions:
# Repository Specific configuration. DevOps can change these as needed
_REPOSITORY: <YOUR_CONTAINER_REPOSITORY_NAME>
_IMAGE_NAME: $(body.payload.properties.imageName)
_REGION: $(body.payload.properties.region)
options:
substitution_option: ALLOW_LOOSE
logging: CLOUD_LOGGING_ONLY
Enabling the webhook trigger for a pipeline
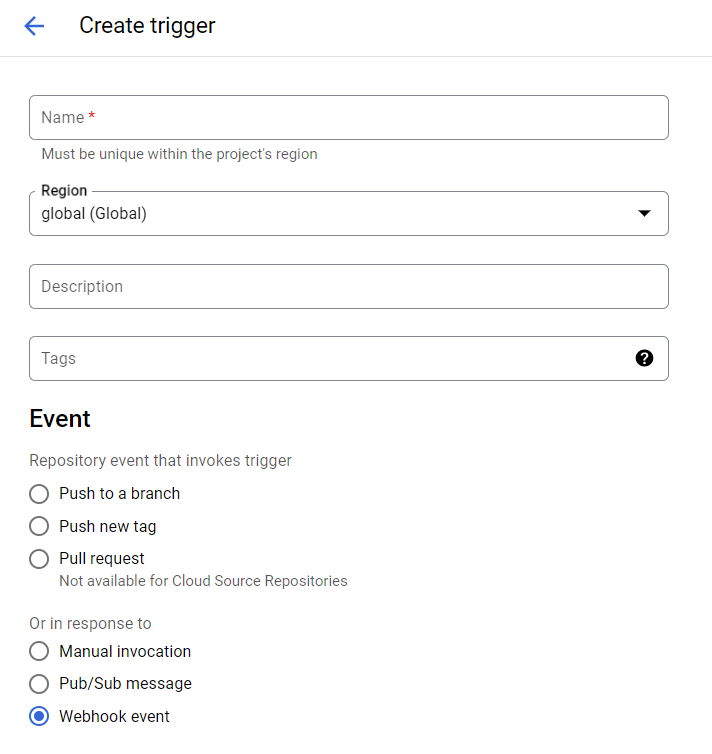
On your Google Cloud Build page, go to the Triggers tab on the left sidebar, click on Create Trigger and fill in the form with the webhook information. Under Event choose "Webhook event"
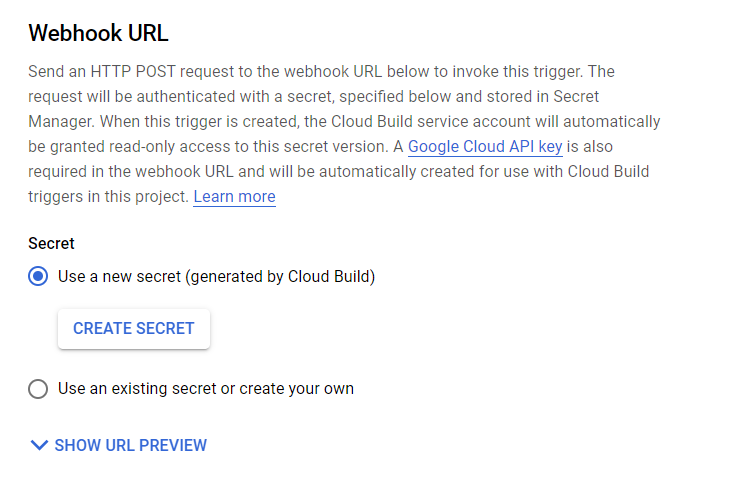
By default, when enabling the webhook trigger for a pipeline, Google requires that you authenticate your webhook URL with a secret. This secret is automatically generated by Cloud Build, and it functions to secure incoming webhook requests.
After you have created or selected an existing secret, you will see a Webhook URL preview. This URL contains an API key generated by Cloud Build and your secret.
Make sure that the service account or API key running the webhook has permission to run Cloud Build pipelines. Follow Google's guideline on how to obtain an API key here
Additionally, if you configure the webhook trigger to use a service account, Google requires that the cloudbuild.yaml file either:
- Specify 'build.logs_bucket'. This option allows you to store the build logs in a Google Cloud Storage bucket. Enable this setting using the following configuration:
steps:
- name: "bash"
args: ["echo", "Hello world!"]
logsBucket: "LOGS_BUCKET_LOCATION"
serviceAccount: "projects/PROJECT_ID/serviceAccounts/SERVICE_ACCOUNT"
options:
logging: GCS_ONLY
- Use the CLOUD_LOGGING_ONLY logging option as shown above;
- Use the NONE logging option.
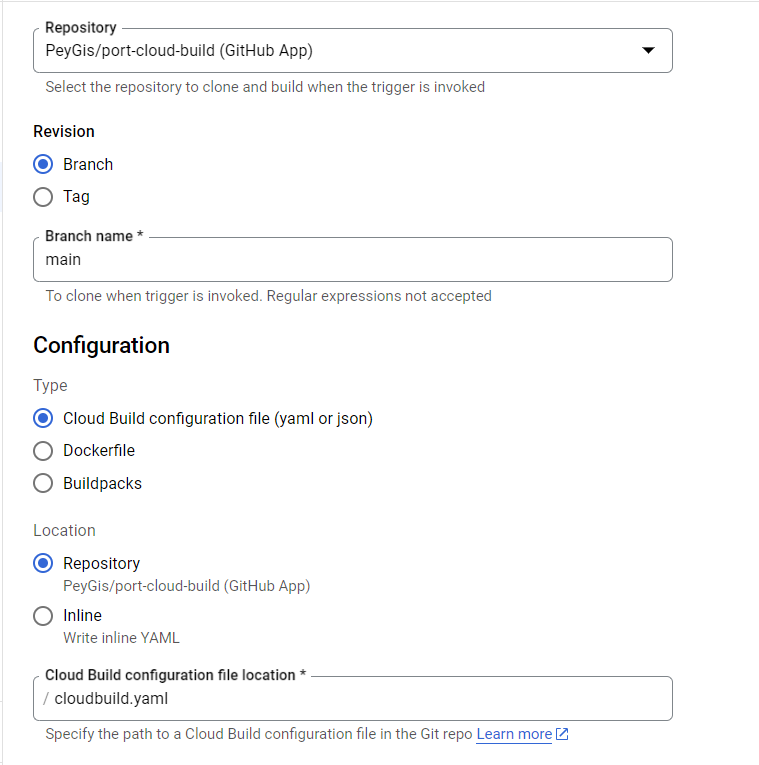
And finally, you need to connect your source code repository to this pipeline and specify whether you want to invoke the pipeline steps in your cloudbuild.yaml or Dockerfile (make sure to mark cloudbuild.yaml if you used the pipeline snippet provided above).
Defining variables
Google Cloud Build enables developers to bind incoming webhook payload data to the pipeline configuration file. If you take a look at the sample cloudbuild.yaml file above, you will see the substitutions section has the below content. This is where you define the variables which will be passed to your pipeline run.
... # Cloud Build pipeline steps
substitutions:
_REPOSITORY: <YOUR_CONTAINER_REPOSITORY_NAME>
_IMAGE_NAME: $(body.payload.properties.imageName)
_REGION: $(body.payload.properties.region)
- The
substitutionsfield value should match the name of the variable that is defined in your pipeline configuration and expected by the job run.
Here is part of the JSON scheme of the Port action, which defines the user inputs that can be used to send in the payload:
{
"identifier": "service_runPipeline",
"title": "Run GCP Cloud Build Pipeline",
"icon": "GCP",
"description": "Webhook trigger for Google Cloud Build",
"trigger": {
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"region": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}
... # Port Action configuration
}
Port Action - The full Port action definition can be found here.
Setting up the Port action
To trigger the Cloud Build pipeline, you will setup a Port Webhook Action.
Here is an example for an action that will trigger the webhook you just set up:
{
"identifier": "service_runPipeline",
"title": "Run GCP Cloud Build Pipeline",
"icon": "GCP",
"description": "Webhook trigger for Google Cloud Build",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "CREATE",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {
"region": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Region Name"
},
"imageName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Container Image Name"
}
},
"required": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "service"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://cloudbuild.googleapis.com/v1/projects/{project_id}/triggers/{webhook_name}:webhook?key={google_api_key}&secret={webhook_secret}",
"body": {
"action": "{{ .action.identifier[(\"service_\" | length):] }}",
"resourceType": "run",
"status": "TRIGGERED",
"trigger": "{{ .trigger | {by, origin, at} }}",
"context": {
"entity": "{{.entity.identifier}}",
"blueprint": "{{.action.blueprint}}",
"runId": "{{.run.id}}"
},
"payload": {
"entity": "{{ (if .entity == {} then null else .entity end) }}",
"action": {
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://cloudbuild.googleapis.com/v1/projects/{project_id}/triggers/{webhook_name}:webhook?key={google_api_key}&secret={webhook_secret}"
},
"trigger": "{{.trigger.operation}}"
},
"properties": {
"{{if (.inputs | has(\"region\")) then \"region\" else null end}}": "{{.inputs.\"region\"}}",
"{{if (.inputs | has(\"imageName\")) then \"imageName\" else null end}}": "{{.inputs.\"imageName\"}}"
},
"censoredProperties": "{{.action.encryptedProperties}}"
}
}
},
"requiredApproval": false,
"publish": true
}
Report CloudBuild run status to Port
Once you have triggered your Cloud Build pipeline successfully, it is essential to update the status of the run action in Port. This update allows Port to monitor the status of your Cloud Build pipeline.
The code snippet below demonstrates how you can report the progress of your pipeline to Port. Remember to modify the Port credentials in the substitutions section for Cloud Build to authenticate using your Port access token.
steps:
# Get Port's Access Token
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/curl"
entrypoint: "bash"
args:
- "-c"
- |
# Get access token and save it to a file
accessToken=$(curl -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"clientId": "${_PORT_CLIENT_ID}", "clientSecret": "${_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET}"}' \
-s 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' | grep -o '"accessToken":"[^"]*' | awk -F'"' '{print $4}')
echo "$accessToken" > /workspace/token.txt
# Logs sending example
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/curl"
args:
- "-c"
- |
curl -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat /workspace/token.txt)" \
-d '{"message": "this is a log test message example"}' \
'https://api.getport.io/v1/actions/runs/${_RUN_ID}/logs'
entrypoint: bash
# Port status update example
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/curl"
args:
- "-c"
- |
curl -X PATCH \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat /workspace/token.txt)" \
-d '{"status":"SUCCESS", "message": {"run_status": "CloudBuild Run completed successfully!"}}' \
'https://api.getport.io/v1/actions/runs/${_RUN_ID}'
entrypoint: bash
substitutions:
_RUN_ID: $(body.context.runId)
_PORT_CLIENT_ID: <Your Port Client Id>
_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET: <Your Port Client Secret>
options:
substitution_option: ALLOW_LOOSE
logging: CLOUD_LOGGING_ONLY
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
That's it! Anytime a user invokes an action in Port UI, a webhook trigger will be sent to Google Cloud Build to execute the pipeline.
For more information, visit: