API
Port's API is a generic interface to model your software catalog, ingest data, invoke actions, query scorecards and more.
💡 Common Port API usage
Since Port API is a generic interface, anything that can be done with Port is possible through the API, for example:
- Update the software catalog using a script.
- Import your existing asset inventory from a CSV file.
- Integrate Port with your custom CI/CD.
- Report the status of a running CI job.
- Update the software catalog about a new build version for a microservice.
- Get existing data from your software catalog.
Get API Token
In order to interact with the API you will need an API token.
Getting an API token involves 2 steps:
- Finding your Port API credentials.
- Making an API request to generate a valid token.
Find your Port credentials
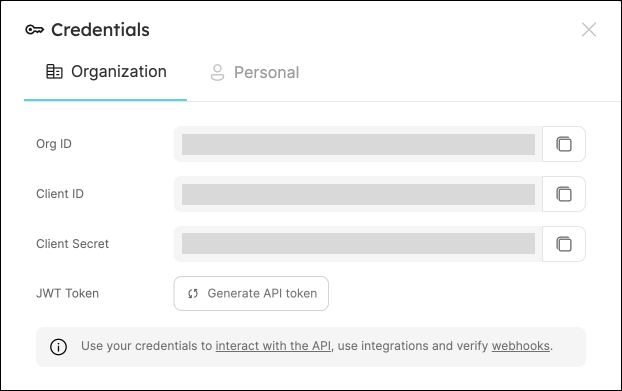
To get your Port credentials, go to your Port application, click on the ... button in the top right corner, and select Credentials. Here you can view and copy your CLIENT_ID and CLIENT_SECRET:
Generate an API token
Here are some code examples showing how to generate an API token in various programming languages:
- Python
- Javascript
- cURL
# Dependencies to install:
# $ python -m pip install requests
import requests
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
# You can now use the value in access_token when making further requests
// Dependencies to install:
// $ npm install axios --save
const axios = require("axios").default;
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID";
const CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET";
const API_URL = "https://api.getport.io/v1";
(async () => {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_URL}/auth/access_token`, {
clientId: CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET,
});
const accessToken = response.data.accessToken;
// You can now use the value in accessToken when making further requests
})();
# Dependencies to install:
# For apt:
# $ sudo apt-get install jq
# For yum:
# $ sudo yum install jq
access_token=$(curl --location --request POST 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"clientId": "CLIENT_ID",
"clientSecret": "CLIENT_SECRET"
}' | jq '.accessToken' | sed 's/"//g')
# The token will be available in the access_token variable
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
Ingest data via API
Since Port is API-first it is possible to create and update entities using simple REST calls from any platform you use.
Setup
To use Port's REST API you need to perform the following steps:
- Find your Port credentials.
- Save them as secrets or in some other same manner such that you can reference them in your code or CI/CD flow.
- Make sure you have an HTTP-capable client.
- For example: cURL, python with the requests package, nodejs with fetch/axios, etc.
Usage
Since you are using Port's REST API directly, any method that the API provides is at your disposal.
We will focus on three specific use cases:
- Get catalog entities - available by making HTTP GET requests to
https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/{blueprint_identifier}/entities/{entity_identifier}, receives the identifier of an existing entity and retrieves it for use in your CI. - Create/Update catalog entities - available by making HTTP POST requests to
https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/{blueprint_identifier}/entities/, receives the identifier and other properties of a new entity or an entity that needs to be updated. - Delete catalog entities - available by making HTTP DELETE requests to
https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/{blueprint_identifier}/entities/{entity_identifier}, receives the identifier of an existing entity and deletes it.
- Get
- Create
- Create/Update
- Create/Override
- Delete
- Delete All
- Python
- Javascript
- cURL
# Dependencies to install:
# $ python -m pip install requests
import requests
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
# You can now use the value in access_token when making further requests
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
blueprint_id = 'MY_BLUEPRINT'
entity_id = 'MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER'
response = requests.get(f'{API_URL}/blueprints/{blueprint_id}/entities/{entity_id}', headers=headers)
# response.json() contains the content of the resulting entity
// Dependencies to install:
// $ npm install axios --save
const axios = require("axios").default;
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID";
const CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET";
const API_URL = "https://api.getport.io/v1";
(async () => {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_URL}/auth/access_token`, {
clientId: CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET,
});
const accessToken = response.data.accessToken;
// You can now use the value in accessToken when making further requests
const blueprintId = "MY_BLUEPRINT";
const entityId = "MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER";
const config = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
};
const getResponse = await axios.get(
`${API_URL}/blueprints/${blueprintId}/entities/${entityId}`,
config
);
// getResponse.data contains the content of the resulting entity
})();
# Dependencies to install:
# for brew:
# brew install jq
# For apt:
# $ sudo apt-get install jq
# For yum:
# $ sudo yum install jq
access_token=$(curl --location --request POST 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"clientId": "CLIENT_ID",
"clientSecret": "CLIENT_SECRET"
}' | jq '.accessToken' | sed 's/"//g')
# The token will be available in the access_token variable
blueprint_id='MY_BLUEPRINT'
entity_id='MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER'
curl --location --request GET "https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/${blueprint_id}/entities/${entity_id}" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json"
# The output of the command contains the content of the resulting entity
A basic create request will create a new entity if one with the provided identifier doesn't exist yet, and will fail with a 409 CONFLICT status code otherwise.
A basic create request is noted by providing no query parameters, or providing the upsert query parameter with its value set to false.
- Python
- Javascript
- cURL
# Dependencies to install:
# $ python -m pip install requests
import requests
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
# You can now use the value in access_token when making further requests
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
blueprint_id = 'MY_BLUEPRINT'
entity = {
'identifier': 'MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER',
'title': 'MY TITLE',
'properties': {
'MY_STRING_PROP': 'MY VALUE',
'MY_BOOLEAN_PROP': False
},
'relations': {}
}
response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/blueprints/{blueprint_id}/entities', json=entity, headers=headers)
# response.json() contains the content of the resulting entity
// Dependencies to install:
// $ npm install axios --save
const axios = require("axios").default;
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID";
const CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET";
const API_URL = "https://api.getport.io/v1";
(async () => {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_URL}/auth/access_token`, {
clientId: CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET,
});
const accessToken = response.data.accessToken;
// You can now use the value in accessToken when making further requests
const blueprintId = "MY_BLUEPRINT";
const config = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
};
const entity = {
identifier: "MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER",
title: "MY TITLE",
properties: {
MY_STRING_PROP: "MY VALUE",
MY_BOOLEAN_PROP: false,
},
relations: {},
};
const postResponse = await axios.post(
`${API_URL}/blueprints/${blueprintId}/entities`,
entity,
config
);
// postResponse.data contains the content of the resulting entity
})();
# Dependencies to install:
# For apt:
# $ sudo apt-get install jq
# For yum:
# $ sudo yum install jq
access_token=$(curl --location --request POST 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"clientId": "CLIENT_ID",
"clientSecret": "CLIENT_SECRET"
}' | jq '.accessToken' | sed 's/"//g')
# The token will be available in the access_token variable
blueprint_id='MY_BLUEPRINT'
curl --location --request POST "https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/${blueprint_id}/entities" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data-raw '{
"identifier": "MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER",
"title": "MY ENTITY TITLE",
"properties": {
"MY_STRING_PROP": "MY VALUE",
"MY_BOOLEAN_PROP": false
}
}'
# The output of the command contains the content of the resulting blueprint
A create/update request will create a new entity if one with the provided identifier doesn't exist yet, and will only update the values of fields provided in the request, if an entity with the identifier already exists.
A create/update request is noted by providing the query parameter: upsert=true&merge=true.
- Python
- Javascript
- cURL
# Dependencies to install:
# $ python -m pip install requests
import requests
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
# You can now use the value in access_token when making further requests
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
blueprint_id = 'MY_BLUEPRINT'
entity = {
'identifier': 'MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER',
'title': 'MY TITLE',
'properties': {
'MY_STRING_PROP': 'MY VALUE',
'MY_BOOLEAN_PROP': False
},
'relations': {}
}
# Note the ?upsert=true&merge=true query parameters
response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/blueprints/{blueprint_id}/entities?upsert=true&merge=true', json=entity, headers=headers)
# response.json() contains the content of the resulting entity
// Dependencies to install:
// $ npm install axios --save
const axios = require("axios").default;
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID";
const CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET";
const API_URL = "https://api.getport.io/v1";
(async () => {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_URL}/auth/access_token`, {
clientId: CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET,
});
const accessToken = response.data.accessToken;
// You can now use the value in accessToken when making further requests
const blueprintId = "MY_BLUEPRINT";
const config = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
};
const entity = {
identifier: "MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER",
title: "MY TITLE",
properties: {
MY_STRING_PROP: "MY VALUE",
MY_BOOLEAN_PROP: false,
},
relations: {},
};
// Note the ?upsert=true&merge=true query parameters
const postResponse = await axios.post(
`${API_URL}/blueprints/${blueprintId}/entities?upsert=true&merge=true`,
entity,
config
);
// postResponse.data contains the content of the resulting entity
})();
# Dependencies to install:
# For apt:
# $ sudo apt-get install jq
# For yum:
# $ sudo yum install jq
access_token=$(curl --location --request POST 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"clientId": "CLIENT_ID",
"clientSecret": "CLIENT_SECRET"
}' | jq '.accessToken' | sed 's/"//g')
# The token will be available in the access_token variable
blueprint_id='MY_BLUEPRINT'
# Note the ?upsert=true&merge=true query parameters
curl --location --request POST "https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/${blueprint_id}/entities?upsert=true&merge=true" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data-raw '{
"identifier": "MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER",
"title": "MY ENTITY TITLE",
"properties": {
"MY_STRING_PROP": "MY VALUE",
"MY_BOOLEAN_PROP": false
}
}'
# The output of the command contains the content of the resulting blueprint
A create/override request will create a new entity if one with the provided identifier doesn't exist yet, and will override all existing values if an entity with the identifier already exists, keeping only the values of fields provided in the request.
A create/override request is noted by providing the query parameter: upsert=true, while not including the merge parameter (or setting its value to false)
- Python
- Javascript
- cURL
# Dependencies to install:
# $ python -m pip install requests
import requests
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
# You can now use the value in access_token when making further requests
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
blueprint_id = 'MY_BLUEPRINT'
entity = {
'identifier': 'MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER',
'title': 'MY TITLE',
'properties': {
'MY_STRING_PROP': 'MY VALUE',
'MY_BOOLEAN_PROP': False
},
'relations': {}
}
# Note the ?upsert=true query parameter
response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/blueprints/{blueprint_id}/entities?upsert=true', json=entity, headers=headers)
# response.json() contains the content of the resulting entity
// Dependencies to install:
// $ npm install axios --save
const axios = require("axios").default;
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID";
const CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET";
const API_URL = "https://api.getport.io/v1";
(async () => {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_URL}/auth/access_token`, {
clientId: CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET,
});
const accessToken = response.data.accessToken;
// You can now use the value in accessToken when making further requests
const blueprintId = "MY_BLUEPRINT";
const config = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
};
const entity = {
identifier: "MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER",
title: "MY TITLE",
properties: {
MY_STRING_PROP: "MY VALUE",
MY_BOOLEAN_PROP: false,
},
relations: {},
};
// Note the ?upsert=true query parameter
const postResponse = await axios.post(
`${API_URL}/blueprints/${blueprintId}/entities?upsert=true`,
entity,
config
);
// postResponse.data contains the content of the resulting entity
})();
# Dependencies to install:
# For apt:
# $ sudo apt-get install jq
# For yum:
# $ sudo yum install jq
access_token=$(curl --location --request POST 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"clientId": "CLIENT_ID",
"clientSecret": "CLIENT_SECRET"
}' | jq '.accessToken' | sed 's/"//g')
# The token will be available in the access_token variable
blueprint_id='MY_BLUEPRINT'
# Note the ?upsert=true query parameter
curl --location --request POST "https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/${blueprint_id}/entities?upsert=true" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data-raw '{
"identifier": "MY_ENTITY_IDENTIFIER",
"title": "MY ENTITY TITLE",
"properties": {
"MY_STRING_PROP": "MY VALUE",
"MY_BOOLEAN_PROP": false
}
}'
# The output of the command contains the content of the resulting blueprint
- Python
- Javascript
- cURL
# Dependencies to install:
# $ python -m pip install requests
import requests
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
# You can now use the value in access_token when making further requests
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
blueprint_id = 'MY_BLUEPRINT'
entity_id = 'MY_ENTITY'
response = requests.delete(f'{API_URL}/blueprints/{blueprint_id}/entities/{entity_id}', headers=headers)
# response.json() contains the content of the resulting entity
// Dependencies to install:
// $ npm install axios --save
const axios = require("axios").default;
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID";
const CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET";
const API_URL = "https://api.getport.io/v1";
(async () => {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_URL}/auth/access_token`, {
clientId: CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET,
});
const accessToken = response.data.accessToken;
// You can now use the value in accessToken when making further requests
const blueprintId = "MY_BLUEPRINT";
const entityId = "MY_ENTITY";
const config = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
};
const deleteResponse = await axios.delete(
`${API_URL}/blueprints/${blueprintId}/entities/${entityId}`,
config
);
// deleteResponse.data contains the content of the resulting entity
})();
# Dependencies to install:
# For apt:
# $ sudo apt-get install jq
# For yum:
# $ sudo yum install jq
access_token=$(curl --location --request POST 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"clientId": "CLIENT_ID",
"clientSecret": "CLIENT_SECRET"
}' | jq '.accessToken' | sed 's/"//g')
# The token will be available in the access_token variable
blueprint_id='MY_BLUEPRINT'
entity_id='MY_ENTITY'
curl --location --request DELETE "https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/${blueprint_id}/entities/${entity_id}" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $access_token"
# The output of the command contains the content of the resulting blueprint
It is possible to delete all entities of a blueprint with a single request using a dedicated route.
It is also possible to delete the blueprint containing the entities within the same delete operation by adding the delete_blueprint=true query parameter, for example: https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/<BLUEPRINT_IDENTIFIER>/all-entities?delete_blueprint=true.
The delete all route can only be used if the blueprint does not have required relations.
- Python
- Javascript
- cURL
# Dependencies to install:
# $ python -m pip install requests
import requests
CLIENT_ID = 'YOUR_CLIENT_ID'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET'
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {'clientId': CLIENT_ID, 'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
# You can now use the value in access_token when making further requests
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
blueprint_id = 'MY_BLUEPRINT'
response = requests.delete(f'{API_URL}/blueprints/{blueprint_id}/all-entities', headers=headers)
# response.json() contains the content of the resulting entity
// Dependencies to install:
// $ npm install axios --save
const axios = require("axios").default;
const CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_CLIENT_ID";
const CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET";
const API_URL = "https://api.getport.io/v1";
(async () => {
const response = await axios.post(`${API_URL}/auth/access_token`, {
clientId: CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET,
});
const accessToken = response.data.accessToken;
// You can now use the value in accessToken when making further requests
const blueprintId = "MY_BLUEPRINT";
const config = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
};
const deleteResponse = await axios.delete(
`${API_URL}/blueprints/${blueprintId}/all-entities`,
config
);
// deleteResponse.data contains the content of the resulting entity
})();
# Dependencies to install:
# For apt:
# $ sudo apt-get install jq
# For yum:
# $ sudo yum install jq
access_token=$(curl --location --request POST 'https://api.getport.io/v1/auth/access_token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"clientId": "CLIENT_ID",
"clientSecret": "CLIENT_SECRET"
}' | jq '.accessToken' | sed 's/"//g')
# The token will be available in the access_token variable
blueprint_id='MY_BLUEPRINT'
curl --location --request DELETE "https://api.getport.io/v1/blueprints/${blueprint_id}/all-entities" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $access_token"
# The output of the command contains the content of the resulting blueprint
It is also possible to delete all entities using Port's web UI:
- Go to the DevPortal Builder page.
- Click on the "Delete All
BLUEPRINT_NAME" button on the desired blueprint. - Follow the instructions.
Note: only users with the admin role can use Port's UI to perform the delete all operation.
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
Rate limits
For more information about Port's rate limits and how to avoid them, check out the rate limits page.