Gitlab CI Pipelines
Using Gitlab CI Pipelines, you can easily create/update and query entities in Port.
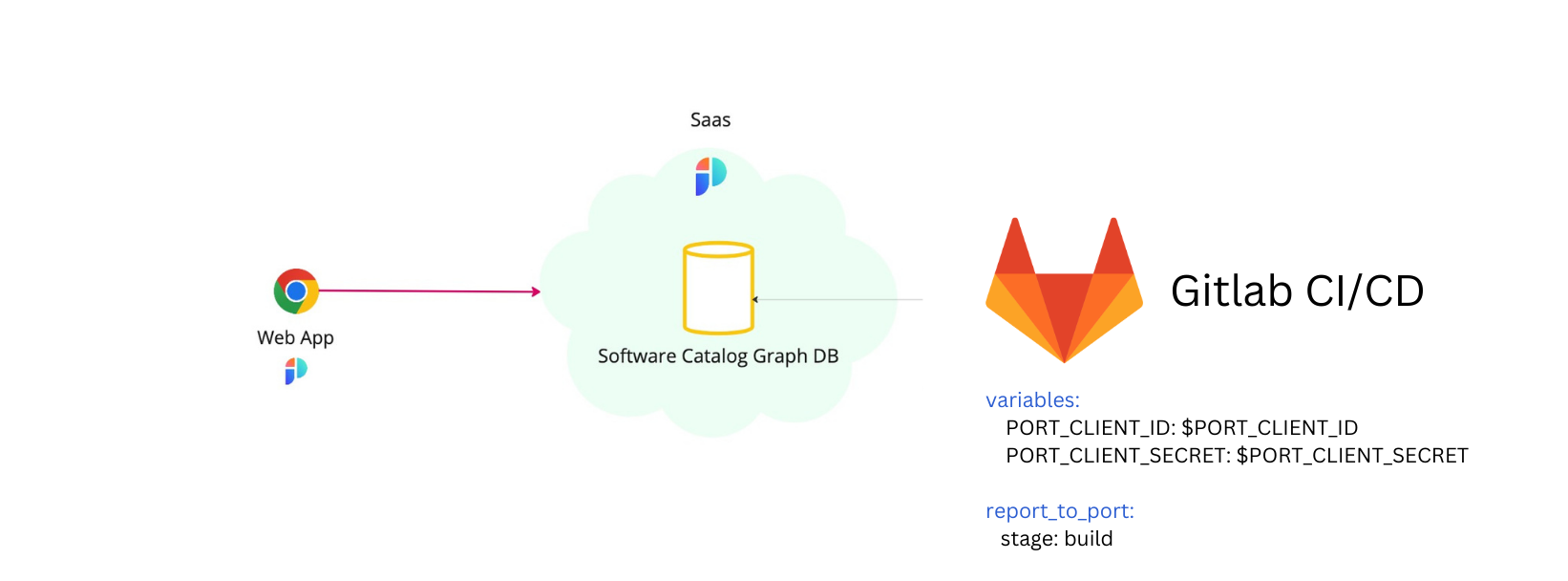
💡 Common Gitlab CI Pipelines usage
Port's API allows for easy integration between Port and your Gitlab CI Pipeline jobs, for example:
- Report the status of a running CI job;
- Update the software catalog about a new build version for a microservice;
- Get existing entities.
Setup
To interact with Port using Gitlab CI Pipeline, you will first need to define your Port credentials as variables for your pipeline.
Then, pass the defined variables to your ci pipeline script, for example, Python:
image: python:3.9
variables:
PORT_CLIENT_ID: $PORT_CLIENT_ID # The variable name for your Port clientId
PORT_CLIENT_SECRET: $PORT_CLIENT_SECRET # The variable name for your Port clientSecret
report_to_port:
stage: build
script:
- python main.py
Make sure you have an existing Blueprint in your Port installation to create/update entities.
Working with Port's API
Here is an example snippet showing how to integrate a job that uses Port's API with your existing Gitlab CI pipelines using Python:
Add the following task to your Gitlab pipeline:
Gitlab pipeline YAML
image: python:3.9
variables:
PORT_CLIENT_ID: $PORT_CLIENT_ID
PORT_CLIENT_SECRET: $PORT_CLIENT_SECRET
stages:
- build
report_to_port:
stage: build
before_script:
- python -m pip install --upgrade pip
- pip install -r requirements.txt
script:
- python main.py
In the following example, we use Python modules which need to be installed. You can use the following requirements.txt:
port_requirements.txt
requests>=2.28.2
- Create/Update
- Get
Create the following Python script in your repository to create or update Port entities as part of your pipeline:
import os
import requests
import json
# These are the credentials passed by the variables of your pipeline to your tasks and in to your env
CLIENT_ID = os.environ['PORT_CLIENT_ID']
CLIENT_SECRET = os.environ['PORT_CLIENT_SECRET']
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {
'clientId': CLIENT_ID,
'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET
}
token_response = requests.post(f"{API_URL}/auth/access_token", json=credentials)
# use this access token + header for all http requests to Port
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
entity_json = {
"identifier": "example-entity",
"properties": {
"myStringProp": "My value",
"myNumberProp": 1,
"myBooleanProp": true,
"myArrayProp": ["myVal1", "myVal2"],
"myObjectProp": {"myKey": "myVal", "myExtraKey": "myExtraVal"}
}
}
# request url : {API_URL}/blueprints/<blueprint_id>/entities
create_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/blueprints/test-blueprint/entities?upsert=true', json=entity_json, headers=headers)
print(json.dumps(get_response.json(), indent=4))
Create the following Python script in your repository to get Port entities as part of your pipeline:
import os
import requests
import json
# These are the credentials passed by the variables of your pipeline to your tasks and in to your env
CLIENT_ID = os.environ['PORT_CLIENT_ID']
CLIENT_SECRET = os.environ['PORT_CLIENT_SECRET']
API_URL = 'https://api.getport.io/v1'
credentials = {
'clientId': CLIENT_ID,
'clientSecret': CLIENT_SECRET
}
token_response = requests.post(f'{API_URL}/auth/access_token', json=credentials)
# use this access token + header for all http requests to Port
access_token = token_response.json()['accessToken']
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
# request url : {API_URL}/blueprints/<blueprint_id>/entities/<entity_id>
get_response = requests.get(f"{API_URL}/blueprints/test-blueprint/entities/test-entity", headers=headers)
print(json.dumps(get_response.json(), indent=4))
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
Examples
Refer to the examples page for practical examples of working with Port using Gitlab CI Pipelines.