Examples
Use the index on the right side of the page to find an example for the resource/s you’re looking to export.
ECS clusters and ECS services
In this step-by-step example, you will export your ECS clusters and ECS services to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- ECS Cluster - will represent ECS clusters from the AWS account.
- ECS Service - will represent ECS services from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
ECS Cluster blueprint
{
"identifier": "ecsCluster",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS ECS Cluster in our software catalog",
"title": "ECS Cluster",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"capacityProviders": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Capacity Providers"
},
"defaultCapacityProviderStrategy": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Default Capacity Provider Strategy"
},
"clusterSettings": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Cluster Settings"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}ECS Service blueprint
{
"identifier": "ecsService",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS ECS Service in our software catalog",
"title": "ECS Service",
"icon": "Service",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"desiredCount": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Desired Count"
},
"taskDefinition": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Task Definition"
},
"launchType": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["EC2", "FARGATE", "EXTERNAL"],
"title": "Launch Type"
},
"schedulingStrategy": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["REPLICA", "DAEMON"],
"title": "Scheduling Strategy"
},
"loadBalancers": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Load Balancers"
},
"securityGroups": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Security Groups"
},
"subnets": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Subnets"
},
"iamRole": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "IAM Role",
"icon": "Unlock"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"ecsCluster": {
"target": "ecsCluster",
"many": false,
"required": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::ECS::Cluster",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".ClusterName",
"title": ".ClusterName",
"blueprint": "ecsCluster",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"capacityProviders": ".CapacityProviders",
"defaultCapacityProviderStrategy": ".DefaultCapacityProviderStrategy",
"clusterSettings": ".ClusterSettings",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".Arn"
}
}
]
}
}
},
{
"kind": "AWS::ECS::Service",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".ServiceName",
"title": ".ServiceName",
"blueprint": "ecsService",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .ServiceArn",
"desiredCount": ".DesiredCount",
"launchType": ".LaunchType",
"cluster": ".Cluster | split(\"/\")[-1]",
"schedulingStrategy": ".SchedulingStrategy",
"loadBalancers": ".LoadBalancers",
"securityGroups": ".NetworkConfiguration.AwsvpcConfiguration.SecurityGroups",
"subnets": ".NetworkConfiguration.AwsvpcConfiguration.Subnets",
"taskDefinition": ".TaskDefinition | split(\"/\")[-1]",
"iamRole": ".Role | if . == null then null else \"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + . end",
"arn": ".ServiceArn"
},
"relations": {
"ecsCluster": ".Cluster | split(\"/\")[-1]"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecs:DescribeClusters",
"ecs:ListClusters",
"ecs:DescribeServices",
"ecs:ListServices"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in ECS clusters and ECS services.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.ecs
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- ecs.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateCluster
- prefix: DeleteCluster
- prefix: UpdateCluster
- prefix: UpdateClusterSettings
- prefix: PutClusterCapacityProviders
- prefix: TagResource
- prefix: UntagResource
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-ecs-cluster-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
clusterName: $.detail.responseElements.cluster.clusterName
eventName: $.detail.eventName
resourceArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceArn
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ECS::Cluster",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<eventName>\" | if test(\"TagResource|UntagResource[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<resourceArn>\" | split(\"/\")[-1] else \"<clusterName>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteCluster[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
EventRule1:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.ecs
detail:
eventSource:
- ecs.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateService
- prefix: UpdateService
- prefix: DeleteService
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-ecs-service-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
clusterArn: $.detail.responseElements.service.clusterArn
eventName: $.detail.eventName
serviceArn: $.detail.responseElements.service.serviceArn
serviceName: $.detail.responseElements.service.serviceName
InputTemplate: >-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ECS::Service",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<eventName>\" | startswith(\"Delete\") then \"<serviceName>\" else \"<serviceArn>|<clusterArn>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | startswith(\"Delete\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any ECS clusters and ECS services.
App Runner services
In this step-by-step example, you will export your App Runner services to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- App Runner - will represent App Runner services from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
App Runner blueprint
{
"identifier": "apprunner",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS App Runner service in our software catalog",
"title": "AppRunner",
"icon": "Service",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"status": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"CREATE_FAILED",
"RUNNING",
"DELETED",
"DELETE_FAILED",
"PAUSED",
"OPERATION_IN_PROGRESS"
],
"enumColors": {
"CREATE_FAILED": "red",
"RUNNING": "green",
"DELETED": "red",
"DELETE_FAILED": "red",
"PAUSED": "yellow",
"OPERATION_IN_PROGRESS": "blue"
},
"title": "Status"
},
"memory": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Memory"
},
"cpu": {
"type": "number",
"title": "CPU"
},
"serviceUrl": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Service URL"
},
"egressType": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["DEFAULT", "VPC"],
"title": "Egress Type"
},
"isPubliclyAccessible": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Is Publicly Accessible"
},
"observabilityEnabled": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Observability Enabled"
},
"autoDeploymentsEnabled": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Auto Deployments Enabled"
},
"healthCheckConfiguration": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Health Check Configuration"
},
"imageConfiguration": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Image Configuration"
},
"imageIdentifier": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Image Identifier"
},
"iamRole": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "IAM Role",
"icon": "Unlock"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::AppRunner::Service",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".ServiceId",
"title": ".ServiceName",
"blueprint": "apprunner",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .ServiceArn",
"status": ".Status",
"memory": ".InstanceConfiguration.Memory",
"cpu": ".InstanceConfiguration.Cpu",
"egressType": ".NetworkConfiguration.EgressConfiguration.EgressType",
"isPubliclyAccessible": ".NetworkConfiguration.IngressConfiguration.IsPubliclyAccessible",
"observabilityEnabled": ".ObservabilityConfiguration.ObservabilityEnabled",
"autoDeploymentsEnabled": ".SourceConfiguration.AutoDeploymentsEnabled",
"healthCheckConfiguration": ".HealthCheckConfiguration",
"imageConfiguration": ".SourceConfiguration.ImageRepository.ImageConfiguration",
"imageIdentifier": ".SourceConfiguration.ImageRepository.ImageIdentifier",
"serviceUrl": "\"https://\" + .ServiceUrl",
"iamRole": ".InstanceConfiguration.InstanceRoleArn | if . == null then null else \"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + . end",
"arn": ".ServiceArn"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["apprunner:DescribeService", "apprunner:ListServices"],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in App Runner services.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AppRunner Service Operation Status Change
source:
- aws.apprunner
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-apprunner-events
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
operationStatus: $.detail.operationStatus
region: $.region
resource: $.resources[0]
serviceId: $.detail.serviceId
InputTemplate: >-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::AppRunner::Service",
"region": "\"<region>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<operationStatus>\" == \"DeleteServiceCompletedSuccessfully\" then \"<serviceId>\" else \"<resource>\" end",
"action": "if \"<operationStatus>\" == \"DeleteServiceCompletedSuccessfully\" then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any App Runner services.
Lambda functions
In this step-by-step example, you will export your Lambda functions to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- Lambda - will represent Lambda functions from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
Lambda blueprint
{
"identifier": "lambda",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS Lambda function in our software catalog",
"title": "Lambda",
"icon": "Lambda",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"description": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Description"
},
"memorySize": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Memory Size"
},
"ephemeralStorageSize": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Ephemeral Storage Size"
},
"timeout": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Timeout"
},
"runtime": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Runtime"
},
"packageType": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["Image", "Zip"],
"title": "Package Type"
},
"environment": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Environment"
},
"architectures": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["x86_64", "arm64"]
},
"title": "Architectures"
},
"layers": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Layers"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"iamRole": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "IAM Role",
"icon": "Unlock"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::Lambda::Function",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".FunctionName",
"title": ".FunctionName",
"blueprint": "lambda",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"description": ".Description",
"memorySize": ".MemorySize",
"ephemeralStorageSize": ".EphemeralStorage.Size",
"timeout": ".Timeout",
"runtime": ".Runtime",
"packageType": ".PackageType",
"environment": ".Environment",
"architectures": ".Architectures",
"layers": ".Layers",
"tags": ".Tags",
"iamRole": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Role",
"arn": ".Arn"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:ListFunctions",
"lambda:GetFunction",
"lambda:GetFunctionCodeSigningConfig"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in Lambda functions.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.lambda
detail:
eventSource:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateFunction
- prefix: UpdateFunctionConfiguration
- prefix: TagResource
- prefix: UntagResource
- prefix: DeleteFunction
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-lambda-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestFunctionName: $.detail.requestParameters.functionName
requestResource: $.detail.requestParameters.resource
responseFunctionName: $.detail.responseElements.functionName
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::Lambda::Function",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<responseFunctionName>\" != \"\" then \"<responseFunctionName>\" elif \"<requestResource>\" != \"\" then \"<requestResource>\" | split(\":\")[-1] else \"<requestFunctionName>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteFunction[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Lambda functions.
SNS topics and SQS queues
In this step-by-step example, you will export your SNS topics and SQS queues to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprints:
- SNS - will represent SNS topics from the AWS account;
- SQS - will represent SQS queues from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
SQS blueprint
{
"identifier": "sqs",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS SQS service in our software catalog",
"title": "SQS",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"fifoQueue": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Fifo Queue"
},
"visibilityTimeout": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Visibility Timeout"
},
"messageRetentionPeriod": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Message Retention Period"
},
"maximumMessageSize": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Maximum Message Size"
},
"receiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Receive Message Wait Time Seconds"
},
"delaySeconds": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Delay Seconds"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}SNS blueprint
{
"identifier": "sns",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS SNS topic in our software catalog",
"title": "SNS",
"icon": "SNS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"fifoTopic": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Fifo Topic"
},
"subscriptions": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Subscriptions"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"sqs": {
"target": "sqs",
"required": false,
"many": true
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::SQS::Queue",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".QueueName",
"title": ".QueueName",
"blueprint": "sqs",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"fifoQueue": ".FifoQueue // false",
"visibilityTimeout": ".VisibilityTimeout",
"messageRetentionPeriod": ".MessageRetentionPeriod",
"maximumMessageSize": ".MaximumMessageSize",
"receiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds": ".ReceiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds",
"delaySeconds": ".DelaySeconds",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".Arn"
}
}
]
}
}
},
{
"kind": "AWS::SNS::Topic",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".TopicName",
"title": ".TopicName",
"blueprint": "sns",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .TopicArn",
"fifoTopic": ".FifoTopic // false",
"subscriptions": ".Subscription",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".TopicArn"
},
"relations": {
"sqs": ".Subscription // [] | map(select(.Protocol == \"sqs\") | .Endpoint | split(\":\")[-1])"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sqs:GetQueueAttributes",
"sqs:ListQueueTags",
"sqs:ListQueues",
"sns:GetDataProtectionPolicy",
"sns:GetTopicAttributes",
"sns:ListSubscriptionsByTopic",
"sns:ListTagsForResource",
"sns:ListTopics"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in SNS topics and SNS queues.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.sns
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- sns.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateTopic
- prefix: Subscribe
- prefix: Unsubscribe
- prefix: TagResource
- prefix: UntagResource
- prefix: DeleteTopic
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-sns-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestResourceArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceArn
requestSubscriptionArn: $.detail.requestParameters.subscriptionArn
requestTopicArn: $.detail.requestParameters.topicArn
responseTopicArn: $.detail.responseElements.topicArn
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::SNS::Topic",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<eventName>\" | if test(\"CreateTopic[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<responseTopicArn>\" elif test(\"Unsubscribe[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<requestSubscriptionArn>\"[:\"<requestSubscriptionArn>\" | rindex(\":\")] elif test(\"TagResource|UntagResource[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<requestResourceArn>\" elif test(\"DeleteTopic[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<requestTopicArn>\" | split(\":\")[-1] else \"<requestTopicArn>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteTopic[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
EventRule1:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.sqs
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- sqs.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateQueue
- prefix: SetQueueAttributes
- prefix: TagQueue
- prefix: UntagQueue
- prefix: DeleteQueue
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-sqs-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestQueueUrl: $.detail.requestParameters.queueUrl
responseQueueUrl: $.detail.responseElements.queueUrl
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::SQS::Queue",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<eventName>\" | if test(\"CreateQueue[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<responseQueueUrl>\" elif test(\"DeleteQueue[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<requestQueueUrl>\" | split(\"/\")[-1] else \"<requestQueueUrl>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteQueue[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any SNS queue and its SQS queues subscriptions.
S3 buckets
In this step-by-step example, you will export your S3 buckets to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- S3 - will represent S3 buckets from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
S3 blueprint
{
"identifier": "s3",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS S3 bucket in our software catalog",
"title": "S3",
"icon": "Bucket",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"regionalDomainName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Regional Domain Name"
},
"versioningStatus": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Versioning Status",
"enum": ["Enabled", "Suspended"]
},
"encryption": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Encryption"
},
"lifecycleRules": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Lifecycle Rules"
},
"publicAccess": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Public Access"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".BucketName",
"title": ".BucketName",
"blueprint": "s3",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"regionalDomainName": ".RegionalDomainName",
"versioningStatus": ".VersioningConfiguration.Status",
"encryption": ".BucketEncryption.ServerSideEncryptionConfiguration",
"lifecycleRules": ".LifecycleConfiguration.Rules",
"publicAccess": ".PublicAccessBlockConfiguration",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".Arn"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"S3:GetBucketWebsite",
"s3:GetAccelerateConfiguration",
"s3:GetAnalyticsConfiguration",
"s3:GetBucketCORS",
"s3:GetBucketLogging",
"s3:GetBucketNotification",
"s3:GetBucketObjectLockConfiguration",
"s3:GetBucketOwnershipControls",
"s3:GetBucketPublicAccessBlock",
"s3:GetBucketTagging",
"s3:GetBucketVersioning",
"s3:GetEncryptionConfiguration",
"s3:GetIntelligentTieringConfiguration",
"s3:GetInventoryConfiguration",
"s3:GetLifecycleConfiguration",
"s3:GetMetricsConfiguration",
"s3:GetReplicationConfiguration",
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in S3 buckets.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.s3
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- s3.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateBucket
- prefix: PutBucket
- prefix: DeleteBucket
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-s3-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestBucketName: $.detail.requestParameters.bucketName
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<requestBucketName>\"",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteBucket[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any S3 buckets.
API Gateway APIs
In this step-by-step example, you will export your API Gateway APIs to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- API Gateway - will represent API Gateway APIs from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
API Gateway blueprint
{
"identifier": "apigateway",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS API Gateway API in our software catalog",
"title": "API Gateway",
"icon": "RestApi",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"description": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Description"
},
"protocolType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Protocol Type",
"enum": ["HTTP", "WEBSOCKET", "REST"]
},
"apiKeySourceType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Api Key Source Type",
"enum": ["HEADER", "AUTHORIZER"]
},
"routeSelection": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Route Selection"
},
"apiEndpoint": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Api Endpoint"
},
"disableExecuteApi": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Disable Execute Api"
},
"cors": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Cors Configuration"
},
"endpointTypes": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Endpoint Types",
"items": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["EDGE", "REGIONAL", "PRIVATE"]
}
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::ApiGateway::RestApi",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".RestApiId",
"title": ".Name",
"blueprint": "apigateway",
"properties": {
"description": ".Description",
"protocolType": "\"REST\"",
"apiKeySourceType": ".ApiKeySourceType",
"disableExecuteApi": ".DisableExecuteApiEndpoint",
"endpointTypes": ".EndpointConfiguration.Types",
"tags": ".Tags"
}
}
]
}
}
},
{
"kind": "AWS::ApiGatewayV2::Api",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".ApiId",
"title": ".Name",
"blueprint": "apigateway",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=arn:aws:apigateway:\" + (.ApiEndpoint | split(\".\")[-3]) + \"::/apis/\" + .ApiId",
"description": ".Description",
"protocolType": ".ProtocolType",
"routeSelection": ".RouteSelectionExpression",
"apiEndpoint": ".ApiEndpoint",
"disableExecuteApi": ".DisableExecuteApiEndpoint",
"cors": ".CorsConfiguration",
"tags": ".Tags | to_entries"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["apigateway:GET"],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in API Gateway APIs.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.apigateway
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- apigateway.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateRestApi
- prefix: ImportRestApi
- prefix: PutRestApi
- prefix: UpdateRestApi
- prefix: DeleteRestApi
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-apigateway-restapi-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestRestApiId: $.detail.requestParameters.restApiId
responseRestApiId: $.detail.responseElements.id
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ApiGateway::RestApi",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<responseRestApiId>\" != \"\" then \"<responseRestApiId>\" else \"<requestRestApiId>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteRestApi[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
EventRule1:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.apigateway
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- apigateway.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateApi
- prefix: ImportApi
- prefix: ReimportApi
- prefix: UpdateApi
- prefix: DeleteApi
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-apigateway-api-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestApiId: $.detail.requestParameters.apiId
responseApiId: $.detail.responseElements.apiId
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ApiGatewayV2::Api",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<responseApiId>\" != \"\" then \"<responseApiId>\" else \"<requestApiId>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteApi[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any API Gateway APIs.
Cloudfront distributions
In this step-by-step example, you will export your Cloudfront distributions to Port.
Cloudfront is a global (not regional) service in AWS, that its events are recorded by AWS CloudTrail in the us-east-1 region.
Therefore, in order to automatically sync changes in Cloudfront distributions with an event rule (step 4 of this example), you need to choose one of the following methods:
- Deploy the Port AWS exporter and the event rule in the
us-east-1region. - Create a trail that will capture global service events in the same region that you've deployed the Port AWS exporter.
For more information, read here.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- Cloudfront - will represent Cloudfront distributions from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
Cloudfront blueprint
{
"identifier": "cloudfront",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS Cloudfront distribution in our software catalog",
"title": "Cloudfront",
"icon": "Cloud",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Link",
"format": "url"
},
"description": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Description"
},
"staging": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Staging"
},
"enabled": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Enabled"
},
"httpVersion": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Http Version",
"enum": ["http1.1", "http2", "http2and3", "http3"]
},
"priceClass": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Price Class",
"enum": ["PriceClass_100", "PriceClass_200", "PriceClass_All"]
},
"domainName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Domain Name"
},
"aliases": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Aliases"
},
"origins": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Origins"
},
"viewerCertificate": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Viewer Certificate"
},
"defaultCacheBehavior": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Default Cache Behavior"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::CloudFront::Distribution",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".Id",
"title": ".Id",
"blueprint": "cloudfront",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=arn:aws:cloudfront:::distribution/\" + .Id",
"description": ".DistributionConfig.Comment",
"staging": ".DistributionConfig.Staging",
"enabled": ".DistributionConfig.Enabled",
"httpVersion": ".DistributionConfig.HttpVersion",
"priceClass": ".DistributionConfig.PriceClass",
"domainName": ".DomainName",
"aliases": ".DistributionConfig.Aliases",
"origins": ".DistributionConfig.Origins",
"viewerCertificate": ".DistributionConfig.ViewerCertificate",
"defaultCacheBehavior": ".DistributionConfig.DefaultCacheBehavior",
"tags": ".Tags"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudfront:GetDistribution*",
"cloudfront:ListDistributions*"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in Cloudfront distributions.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.cloudfront
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- cloudfront.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateDistribution
- prefix: CopyDistribution
- prefix: UpdateDistribution
- prefix: DeleteDistribution
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-cloudfront-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestDistributionId: $.detail.requestParameters.id
responseDistributionId: $.detail.responseElements.distribution.id
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::CloudFront::Distribution",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<responseDistributionId>\" != \"\" then \"<responseDistributionId>\" else \"<requestDistributionId>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteDistribution[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Cloudfront distributions.
DynamoDB tables
In this step-by-step example, you will export your DynamoDB tables to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- DynamoDB - will represent DynamoDB tables from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
DynamoDB blueprint
{
"identifier": "dynamodb",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS DynamoDB table in our software catalog",
"title": "DynamoDB",
"icon": "SQL",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Link",
"format": "url"
},
"writeCapacityUnits": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Write Capacity Units"
},
"readCapacityUnits": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Read Capacity Units"
},
"deletionProtectionEnabled": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Deletion Protection Enabled"
},
"pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Point In Time Recovery Enabled"
},
"ttlEnabled": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "TTL Enabled"
},
"ttlAttributeName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "TTL Attribute Name"
},
"billingMode": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Billing Mode",
"enum": ["PAY_PER_REQUEST", "PROVISIONED"]
},
"attributeDefinitions": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Attribute Definitions"
},
"keySchema": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Key Schema"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::DynamoDB::Table",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".TableName",
"title": ".TableName",
"blueprint": "dynamodb",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"writeCapacityUnits": ".ProvisionedThroughput.WriteCapacityUnits",
"readCapacityUnits": ".ProvisionedThroughput.ReadCapacityUnits",
"deletionProtectionEnabled": ".DeletionProtectionEnabled",
"pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled": ".PointInTimeRecoverySpecification.PointInTimeRecoveryEnabled",
"ttlEnabled": ".TimeToLiveSpecification.Enabled",
"ttlAttributeName": ".TimeToLiveSpecification.AttributeName",
"billingMode": ".BillingMode",
"attributeDefinitions": ".AttributeDefinitions",
"keySchema": ".KeySchema",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".Arn"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:DescribeContinuousBackups",
"dynamodb:DescribeContributorInsights",
"dynamodb:DescribeTable",
"dynamodb:DescribeTimeToLive",
"dynamodb:ListTables",
"dynamodb:ListTagsOfResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in DynamoDB tables.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.dynamodb
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- dynamodb.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateTable
- prefix: UpdateTable
- prefix: UpdateTimeToLive
- prefix: UpdateContinuousBackups
- prefix: TagResource
- prefix: UntagResource
- prefix: DeleteTable
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-dynamodb-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestResourceArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceArn
requestTableName: $.detail.requestParameters.tableName
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::DynamoDB::Table",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<requestTableName>\" != \"\" then \"<requestTableName>\" else \"<requestResourceArn>\" | split(\"/\")[-1] end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteTable[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any DynamoDB tables.
RDS instances
In this step-by-step example, you will export your RDS instances to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- RDS - will represent RDS instances from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
RDS blueprint
{
"identifier": "rds",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS RDS instance in our software catalog",
"title": "RDS",
"icon": "SQL",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Link",
"format": "url"
},
"engine": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Engine"
},
"engineVersion": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Engine Version"
},
"storageType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Storage Type",
"enum": ["gp2", "gp3", "io1", "standard", "aurora"]
},
"dbInstanceClass": {
"type": "string",
"title": "DB Instance Class"
},
"availabilityZone": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Availability Zone"
},
"dbParameterGroup": {
"type": "string",
"title": "DB Parameter Group"
},
"optionGroup": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Option Group"
},
"dbSubnetGroup": {
"type": "string",
"title": "DB Subnet Group"
},
"masterUsername": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Master Username"
},
"allocatedStorage": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Allocated Storage"
},
"maxAllocatedStorage": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Max Allocated Storage"
},
"backupRetentionPeriod": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Backup Retention Period"
},
"monitoringInterval": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Monitoring Interval",
"enum": [0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60]
},
"multiAZ": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Multi AZ"
},
"storageEncrypted": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Storage Encrypted"
},
"enablePerformanceInsights": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Enable Performance Insights"
},
"autoMinorVersionUpgrade": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Auto Minor Version Upgrade"
},
"deletionProtection": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Deletion Protection"
},
"publiclyAccessible": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Publicly Accessible"
},
"certificateValidTill": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Certificate Valid Till",
"format": "date-time"
},
"certificateCA": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Certificate CA"
},
"preferredBackupWindow": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Preferred Backup Window"
},
"preferredMaintenanceWindow": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Preferred Maintenance Window"
},
"endpoint": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Endpoint"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::RDS::DBInstance",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".DBInstanceIdentifier",
"title": ".DBInstanceIdentifier",
"blueprint": "rds",
"properties": {
"link": "if .Engine == \"docdb\" then \"https://console.aws.amazon.com/docdb/home?region=\" + (.DBInstanceIdentifier | split(\":\")[3]) + \"#instance-details/\" + .DBInstanceIdentifier else \"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .DBInstanceArn end",
"engine": ".Engine",
"engineVersion": ".EngineVersion",
"storageType": ".StorageType",
"dbInstanceClass": ".DBInstanceClass",
"availabilityZone": ".AvailabilityZone",
"dbParameterGroup": ".DBParameterGroupName",
"optionGroup": ".OptionGroupName",
"dbSubnetGroup": ".DBSubnetGroupName",
"masterUsername": ".MasterUsername",
"allocatedStorage": ".AllocatedStorage",
"maxAllocatedStorage": ".MaxAllocatedStorage",
"backupRetentionPeriod": ".BackupRetentionPeriod",
"monitoringInterval": ".MonitoringInterval",
"multiAZ": ".MultiAZ",
"storageEncrypted": ".StorageEncrypted",
"enablePerformanceInsights": ".EnablePerformanceInsights",
"autoMinorVersionUpgrade": ".AutoMinorVersionUpgrade",
"deletionProtection": ".DeletionProtection",
"publiclyAccessible": ".PubliclyAccessible",
"certificateValidTill": ".CertificateDetails.ValidTill",
"certificateCA": ".CertificateDetails.CAIdentifier",
"preferredBackupWindow": ".PreferredBackupWindow",
"preferredMaintenanceWindow": ".PreferredMaintenanceWindow",
"endpoint": ".Endpoint",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".DBInstanceArn"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:DescribeAccountAttributes",
"ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones",
"ec2:DescribeInternetGateways",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeVpcAttribute",
"ec2:DescribeVpcs",
"rds:DescribeDBInstances"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in RDS instances.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.rds
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- rds.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateDBInstance
- prefix: CreateDBInstanceReadReplica
- prefix: RestoreDBInstanceFromDBSnapshot
- prefix: RestoreDBInstanceFromS3
- prefix: RestoreDBInstanceToPointInTime
- prefix: ModifyDBInstance
- prefix: AddTagsToResource
- prefix: RemoveTagsFromResource
- prefix: DeleteDBInstance
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-rds-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestDBInstanceIdentifier: $.detail.requestParameters.dBInstanceIdentifier
requestResourceName: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceName
requestTargetDBInstanceIdentifier: $.detail.requestParameters.targetDBInstanceIdentifier
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::RDS::DBInstance",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<requestTargetDBInstanceIdentifier>\" != \"\" then \"<requestTargetDBInstanceIdentifier>\" elif \"<requestDBInstanceIdentifier>\" != \"\" then \"<requestDBInstanceIdentifier>\" else \"<requestResourceName>\" | split(\":\")[-1] end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteDBInstance[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any RDS instances.
Step Functions state machines
In this step-by-step example, you will export your Step Functions state machines to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- Step Functions - will represent Step Functions state machines from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
Step Functions blueprint
{
"identifier": "stepfunctions",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS Step Functions state machine in our software catalog",
"title": "Step Functions",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Link",
"format": "url"
},
"type": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Type",
"enum": ["STANDARD", "EXPRESS"]
},
"definitionS3Location": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Definition S3 Location"
},
"definitionObject": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Definition Object"
},
"definitionSubstitutions": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Definition Substitutions"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"iamRole": {
"type": "string",
"title": "IAM Role",
"format": "url",
"icon": "Unlock"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::StepFunctions::StateMachine",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".StateMachineName",
"title": ".StateMachineName",
"blueprint": "stepfunctions",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"type": ".StateMachineType",
"definitionS3Location": ".DefinitionS3Location",
"definitionObject": ".DefinitionString | fromjson",
"definitionSubstitutions": ".DefinitionSubstitutions",
"tags": ".Tags",
"iamRole": ".RoleArn | if . == null then null else \"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + . end",
"arn": ".Arn"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"states:DescribeStateMachine",
"states:ListStateMachines",
"states:ListTagsForResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in Step Functions state machines.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.states
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- states.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateStateMachine
- prefix: UpdateStateMachine
- prefix: TagResource
- prefix: UntagResource
- prefix: DeleteStateMachine
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-stepfunctions-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestResourceArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceArn
requestStateMachineArn: $.detail.requestParameters.stateMachineArn
responseStateMachineArn: $.detail.responseElements.stateMachineArn
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::StepFunctions::StateMachine",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<eventName>\" | if test(\"DeleteStateMachine[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"<requestStateMachineArn>\" | split(\":\")[-1] elif \"<responseStateMachineArn>\" != \"\" then \"<responseStateMachineArn>\" elif \"<requestStateMachineArn>\" != \"\" then \"<requestStateMachineArn>\" else \"<requestResourceArn>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteStateMachine[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Step Functions state machines.
Elastic Beanstalk applications and environments
In this step-by-step example, you will export your Elastic Beanstalk applications and environments to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- Beanstalk Application - will represent Elastic Beanstalk applications from the AWS account.
- Beanstalk Environment - will represent Elastic Beanstalk environments from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
Beanstalk Application blueprint
{
"identifier": "beanstalkApplication",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS Elastic Beanstalk application in our software catalog",
"title": "Beanstalk Application",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Description"
},
"versionMaxCountRule": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Version Max Count Rule"
},
"versionMaxAgeRule": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Version Max Age Rule"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}Beanstalk Environment blueprint
{
"identifier": "beanstalkEnvironment",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS Elastic Beanstalk environment in our software catalog",
"title": "Beanstalk Environment",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Description"
},
"solutionStackName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Solution Stack Name"
},
"tierName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Tier Name",
"enum": ["WebServer", "Worker"]
},
"tierType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Tier Type",
"enum": ["Standard", "SQS/HTTP"]
},
"endpointURL": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Endpoint URL"
},
"cnamePrefix": {
"type": "string",
"title": "CNAME Prefix"
},
"platformArn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Platform Arn"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"beanstalkApplication": {
"target": "beanstalkApplication",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::ElasticBeanstalk::Application",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".ApplicationName",
"title": ".ApplicationName",
"blueprint": "beanstalkApplication",
"properties": {
"description": ".Description",
"versionMaxCountRule": ".ResourceLifecycleConfig.VersionLifecycleConfig.MaxAgeRule",
"versionMaxAgeRule": ".ResourceLifecycleConfig.VersionLifecycleConfig.MaxCountRule"
}
}
]
}
}
},
{
"kind": "AWS::ElasticBeanstalk::Environment",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".EnvironmentName",
"title": ".EnvironmentName",
"blueprint": "beanstalkEnvironment",
"properties": {
"description": ".Description",
"cnamePrefix": ".CNAMEPrefix",
"solutionStackName": ".SolutionStackName",
"platformArn": ".PlatformArn",
"tierName": ".Tier.Name",
"tierType": ".Tier.Type",
"endpointURL": ".EndpointURL",
"tags": ".Tags"
},
"relations": {
"beanstalkApplication": ".ApplicationName"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"elasticbeanstalk:DescribeApplications",
"elasticbeanstalk:DescribeConfigurationSettings",
"elasticbeanstalk:DescribeEnvironments",
"elasticbeanstalk:ListTagsForResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in Elastic Beanstalk applications and environments.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticbeanstalk
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticbeanstalk.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateApplication
- prefix: UpdateApplication
- prefix: UpdateApplicationResourceLifecycle
- prefix: DeleteApplication
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-beanstalk-apps-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestApplicationName: $.detail.requestParameters.applicationName
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElasticBeanstalk::Application",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<requestApplicationName>\"",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteApplication[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
EventRule1:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticbeanstalk
detail-type:
- Elastic Beanstalk resource status change
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-beanstalk-envs-events
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
environmentName: $.detail.EnvironmentName
region: $.region
status: $.detail.Status
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElasticBeanstalk::Environment",
"region": "\"<region>\"",
"identifier": "\"<environmentName>\"",
"action": "if \"<status>\" == \"Environment termination successful\" then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Elastic Beanstalk applications and environments.
CloudFormation Stacks
In this step-by-step example, you will export your CloudFormation Stacks to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- CloudFormation Stack - will represent CloudFormation Stacks from the AWS account.
You may use the following definition:
CloudFormationStack blueprint
{
"identifier": "cloudFormationStack",
"description": "This blueprint represents a service in our software catalog",
"title": "CloudFormation Stack",
"icon": "Microservice",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"createdAt": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Creation Time"
},
"status": {
"title": "Status",
"description": "The current status of the Stack",
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"CREATE_IN_PROGRESS",
"CREATE_FAILED",
"CREATE_COMPLETE",
"ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS",
"ROLLBACK_FAILED",
"ROLLBACK_COMPLETE",
"DELETE_IN_PROGRESS",
"DELETE_FAILED",
"UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS",
"UPDATE_COMPLETE_CLEANUP_IN_PROGRESS",
"UPDATE_COMPLETE",
"UPDATE_FAILED",
"UPDATE_ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS",
"UPDATE_ROLLBACK_FAILED",
"UPDATE_ROLLBACK_COMPLETE_CLEANUP_IN_PROGRESS",
"UPDATE_ROLLBACK_COMPLETE",
"REVIEW_IN_PROGRESS",
"IMPORT_IN_PROGRESS",
"IMPORT_COMPLETE",
"IMPORT_ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS",
"IMPORT_ROLLBACK_FAILED",
"IMPORT_ROLLBACK_COMPLETE"
],
"enumColors": {
"CREATE_IN_PROGRESS": "orange",
"CREATE_FAILED": "red",
"CREATE_COMPLETE": "green",
"ROLLBACK_IN_PROGRESS": "orange",
"ROLLBACK_FAILED": "red",
"ROLLBACK_COMPLETE": "green",
"UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS": "orange",
"UPDATE_FAILED": "red",
"UPDATE_COMPLETE": "green"
}
},
"template": {
"title": "Template",
"type": "string",
"format": "yaml"
},
"tags": {
"items": {
"type": "object"
},
"title": "Tags",
"type": "array"
},
"link": {
"title": "link",
"description": "The aws console stack url",
"type": "string",
"format": "url"
},
"lastUpdated": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Last Updated"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"kind": "AWS::CloudFormation::Stack",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".StackName",
"title": ".StackName",
"blueprint": "cloudFormationStack",
"properties": {
"lastUpdated": ".LastUpdatedTime",
"createdAt": ".CreationTime",
"status": ".StackStatus",
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .StackId",
"template": ".TemplateBody",
"tags": ".Tags"
}
}
]
}
}
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackResources",
"cloudformation:ListStacks",
"cloudformation:GetTemplate"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: Create 2 event rules to trigger automatic syncing of changes in CloudFormation Stacks.
You may use the following CloudFormation Template:
Event Rule CloudFormation Template
EventRule0:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.cloudformation
detail:
eventSource:
- cloudformation.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateStack
- prefix: UpdateStack
- prefix: DeleteStack
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-cloudformation-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
eventName: $.detail.eventName
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
stackName: $.detail.requestParameters.stackName
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::CloudFormation::Stack",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "if \"<stackName>\" | startswith(\"arn:\") then \"<stackName>\" | split(\"/\")[1] else \"<stackName>\" end",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteStack[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
EventRule1:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- CloudFormation Stack Status Change
source:
- aws.cloudformation
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-cloudformation-status-change-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
region: $.region
stackId: $.detail.stack-id
status: $.detail.status-details.status
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::CloudFormation::Stack",
"region": "\"<region>\"",
"identifier": "\"<stackId>\" | split(\"/\")[1]",
"action": "if \"<status>\" == \"DELETE_COMPLETE\" then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
The AWS CloudFormation API can retrieve up to 100 resources per CloudFormation Stack.
For more information about the CloudFormation API, see the API Reference.
Relations between CloudFormation Stacks and AWS resources
In order to connect between CloudFormation Stacks and their affected resources, you'll need to update the blueprint and the exporter configuration.
Here's an example showing how to connect CloudFormation Stacks and Lambda functions:
Add relations to the blueprint
{
"relations": {
"lambdas": {
"title": "Created Lambdas",
"description": "The Lambda functions created from the CloudFormation Stack",
"target": "lambda",
"required": false,
"many": true
}
}
}
Add relations to the exporter config.json
{
...
"mappings": [
{...},
"relations": {
"lambdas": ".StackResources // [] | map(select(.ResourceType == \"AWS::Lambda::Function\")) | if . == [] then [] else .[].PhysicalResourceId end"
}]
}
Make sure your Lambda function configuration appears before your CloudFormation definition in the config.json.
Done! soon, you will be able to see any CloudFormation Stacks.
EC2 instances
In this step-by-step example, you will export your EC2 instances to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- EC2 Instance - will represent EC2 instances from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
EC2 instance blueprint
{
"identifier": "ec2Instance",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS EC2 instance in our software catalog",
"title": "EC2 Instance",
"icon": "EC2",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"architecture": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Architecture",
"enum": ["i386", "x86_64", "arm64", "x86_64_mac", "arm64_mac"]
},
"availabilityZone": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Availability Zone"
},
"link": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Link",
"format": "url"
},
"platform": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Platform"
},
"state": {
"type": "string",
"title": "State",
"enum": [
"pending",
"running",
"shutting-down",
"terminated",
"stopping",
"stopped"
],
"enumColors": {
"pending": "yellow",
"running": "green",
"shutting-down": "pink",
"stopped": "purple",
"stopping": "orange",
"terminated": "red"
}
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"type": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Instance Type"
},
"vpcId": {
"type": "string",
"title": "VPC ID"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::EC2::Instance",
"selector": {
"query": ".State.Name | startswith(\"terminated\") | not"
},
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".InstanceId",
"title": ".Tags[]? | select(.Key == \"Name\") | .Value",
"blueprint": "ec2Instance",
"properties": {
"state": ".State.Name",
"type": ".InstanceType",
"vpcId": ".VpcId",
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/home?region=\" + .Placement.AvailabilityZone[:-1] + \"#InstanceDetails:instanceId=\" + .InstanceId",
"availabilityZone": ".Placement.AvailabilityZone",
"platform": ".PlatformDetails",
"architecture": ".Architecture",
"tags": ".Tags"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ec2:DescribeInstances", "ec2:DescribeInstanceStatus"],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in EC2 instances.
You may use the following CloudFormation template:
Event rule CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EC2InstanceTagsEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.ec2
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- ec2.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: DeleteTags
- prefix: CreateTags
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-ec2-tags-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestInstanceId: $.detail.requestParameters.resourcesSet.items[0].resourceId
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::EC2::Instance",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<requestInstanceId>\"",
"action": "\"upsert\""
}
EC2InstanceStateChangeEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- EC2 Instance State-change Notification
source:
- aws.ec2
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-ec2-instance-status-change-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
region: $.region
instanceId: $.detail.instance-id
status: $.detail.state
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::EC2::Instance",
"region": "\"<region>\"",
"identifier": "\"<instanceId>\"",
"action": "if \"<status>\" == \"terminated\" then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any EC2 instances
Elastic load balancers
In this step-by-step example, you will export your Load balancers to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
- Load Balancer - will represent load balancers from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
LoadBalancer blueprint
{
"identifier": "loadBalancer",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS Load Balancer in our software catalog",
"title": "Load Balancer",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"state": {
"type": "string",
"title": "State",
"default": "active",
"enum": ["provisioning", "active", "failed", "active_impaired"],
"enumColors": {
"active": "green",
"failed": "red",
"provisioning": "yellow",
"active_impaired": "orange"
}
},
"type": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Type",
"default": "application",
"enum": ["application", "network", "gateway"]
},
"scheme": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Scheme"
},
"vpcId": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Vpc ID"
},
"availabilityZones": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Availability Zones"
},
"dnsName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "DNS Name"
},
"securityGroup": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Security Group"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
},
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"listeners": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Listeners"
},
"attributes": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Attributes"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"region": {
"title": "Region",
"target": "region",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".LoadBalancerName",
"title": ".LoadBalancerName",
"blueprint": "loadBalancer",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .LoadBalancerArn",
"state": ".State.Code",
"type": ".Type",
"scheme": ".Scheme",
"vpcId": ".VpcId",
"availabilityZones": ".AvailabilityZones",
"dnsName": ".DNSName",
"securityGroup": ".SecurityGroups",
"listeners": ".Listeners",
"attributes": ".Attributes",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".LoadBalancerArn"
},
"relations": {
"region": ".LoadBalancerArn | split(\":\") | .[3]"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListeners",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in load balancers.
You may use the following CloudFormation template:
Event rule CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
LoadBalancerCreateEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticloadbalancing
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateLoadBalancer
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-elb-create-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestElbName: $.detail.requestParameters.name
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<requestElbName>\"",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteLoadBalancer[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
LoadBalancerUpdateEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticloadbalancing
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: DeleteLoadBalancer
- prefix: SetSecurityGroups
- prefix: ModifyLoadBalancerAttributes
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-elb-update-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestElbArn: $.detail.requestParameters.loadBalancerArn
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<requestElbArn>\" | split(\"/\") | .[2]",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteLoadBalancer[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
LoadBalancerTagsEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticloadbalancing
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: RemoveTags
- prefix: AddTags
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-elb-tags-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestElbArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceArns[0]
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<requestElbArn>\" | split(\"/\") | .[2]",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteLoadBalancer[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
LoadBalancerUpsertListenersEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticloadbalancing
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateListener
- prefix: ModifyListener
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-elb-upsert-listener-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
responseElbArn: $.detail.responseElements.listeners[0].loadBalancerArn
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<responseElbArn>\" | split(\"/\") | .[2]",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteLoadBalancer[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
LoadBalancerDeleteListenersEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticloadbalancing
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: DeleteListener
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-elb-delete-listener-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
requestElbArn: $.detail.requestParameters.listenerArn
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<requestElbArn>\" | split(\"/\") | .[2]",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | test(\"DeleteLoadBalancer[^a-zA-Z]*$\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Load balancers
EKS clusters
In this step-by-step example, you will export your EKS clusters to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
EKS Cluster - will represent EKS clusters from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
EKS blueprint
{
"identifier": "eks",
"description": "",
"title": "EKS Cluster",
"icon": "Service",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Name"
},
"roleArn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Role ARN"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
},
"version": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Version"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"region": {
"title": "Region",
"target": "region",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::EKS::Cluster",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".Name",
"title": ".Name",
"blueprint": "eks",
"properties": {
"name": ".Name",
"roleArn": ".RoleArn",
"version": ".Version",
"tags": ".Tags"
}
}
],
"relations": {
"region": ".Arn | split(\":\")[3]",
"cloudAccount": ".Arn | split(\":\")[4]"
}
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["eks:DescribeCluster", "eks:ListClusters"],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in EKS clusters.
You may use the following CloudFormation template:
Event rule CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
EksClusterEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.eks
detail:
eventSource:
- eks.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateCluster
- prefix: DeleteCluster
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-eks-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
clusterArn: $.detail.responseElements.cluster.arn
eventName: $.detail.eventName
clusterName: $.detail.responseElements.cluster.name
InputTemplate: >-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::EKS::Cluster",
"region": "<awsRegion>",
"identifier": "<clusterName>",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | startswith(\"Delete\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any EKS clusters
ECR repositories
In this step-by-step example, you will export your ECR repositories to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
ECR Repository - will represent ECR repositories from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
ECR Repository blueprint
{
"identifier": "ecr_repository",
"title": "ECR Repository",
"icon": "Service",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"title": "Link",
"type": "string",
"format": "url"
},
"imageTagMutability": {
"title": "Image Tag Mutability",
"type": "string"
},
"scanningConfiguration": {
"title": "Scanning Configuration",
"type": "object"
},
"repositoryArn": {
"title": "Repository ARN",
"type": "string"
},
"repositoryUri": {
"title": "Repository URI",
"type": "string"
},
"encryptionConfiguration": {
"title": "Encryption Configuration",
"type": "object"
},
"lifecyclePolicy": {
"title": "Lifecycle Policy",
"type": "object"
},
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "array"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"region": {
"title": "Region",
"target": "region",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::ECR::Repository",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".RepositoryName",
"title": ".RepositoryName",
"blueprint": "ecr_repository",
"properties": {
"imageTagMutability": ".ImageTagMutability",
"scanningConfiguration": ".ImageScanningConfiguration",
"repositoryArn": ".Arn",
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"repositoryUri": ".RepositoryUri",
"encryptionConfiguration": ".EncryptionConfiguration",
"lifecyclePolicy": ".LifecyclePolicy",
"tags": ".Tags"
},
"relations": {
"region": ".Arn | split(\":\") | .[3]"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:DescribeRepositories",
"ecr:GetLifecyclePolicy",
"ecr:GetRepositoryPolicy",
"ecr:ListTagsForResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in ECR repositories.
You may use the following CloudFormation template:
Event rule CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
ECRRepositoryEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.ecr
detail:
eventSource:
- ecr.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateRepository
- prefix: DeleteRepository
- prefix: DeleteLifecyclePolicy
- prefix: PutLifecyclePolicy
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-ecr-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
repositoryName: $.detail.requestParameters.repositoryName
InputTemplate: >-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ECR::Repository",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<repositoryName>\"",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | startswith(\"DeleteRepository\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
ECRRepositoryTagRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.ecr
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- ecr.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: TagResource
- prefix: UntagResource
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-ecr-tags-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
resourceArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceArn
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ECR::Repository",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<resourceArn>\" | split(\"/\") | .[-1]",
"action": "\"upsert\""
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any ECR repositories
Using Python script
Alternatively you can use a Python script to export your ECR repositories and images to Port. The script is available in the example-ecr-images repository.
Elasticache serverless cache
In this step-by-step example, you will export your Serverless cache to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
Serverless cache - will represent Serverless cache from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
Serverless cache blueprint
{
"identifier": "aws_elasticache",
"title": "Serverless Cache",
"icon": "Service",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"status": {
"title": "Status",
"type": "string"
},
"description": {
"title": "Description",
"type": "string"
},
"engine": {
"title": "Engine",
"type": "string"
},
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "array"
},
"link": {
"title": "Link",
"type": "string",
"format": "url"
},
"majorEngineVersion": {
"title": "Major Engine Version",
"type": "string"
},
"arn": {
"title": "ARN",
"type": "string"
},
"createdTime": {
"title": "Created Time",
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
},
"dailySnapshotTime": {
"title": "Daily Snapshot Time",
"type": "string"
},
"readerEndpoint": {
"title": "Reader Endpoint",
"type": "object"
},
"endpoint": {
"title": "Endpoint",
"type": "object"
},
"securityGroup": {
"title": "Security Group",
"type": "array"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"region": {
"title": "Region",
"target": "region",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::ElastiCache::ServerlessCache",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".ServerlessCacheName",
"title": ".ServerlessCacheName",
"blueprint": "aws_elasticache",
"properties": {
"status": ".Status",
"description": ".Description",
"majorEngineVersion": ".MajorEngineVersion",
"createdTime": ".CreateTime",
"dailySnapshotTime": ".DailySnapshotTime",
"readerEndpoint": ".ReaderEndpoint",
"endpoint": ".Endpoint",
"securityGroup": ".SecurityGroupIds",
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .ARN",
"arn": ".ARN",
"engine": ".Engine",
"tags": ".Tags"
},
"relations": {
"region": ".ARN | split(\":\") | .[3]"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"elasticache:DescribeServerlessCaches",
"elasticache:ListTagsForResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in Elasticache serverless caches.
You may use the following CloudFormation template:
Event rule CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
ElasticacheEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.elasticache
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticache.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateServerlessCache
- prefix: DeleteServerlessCache
- prefix: ModifyServerlessCache
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-serverless-cache-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
cacheName: $.detail.responseElements.serverlessCache.serverlessCacheName
InputTemplate: >-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElastiCache::ServerlessCache",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<cacheName>\"",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | startswith(\"DeleteServerlessCache\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
ElasticacheTagRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticache
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticache.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: AddTagsToResource
- prefix: RemoveTagsFromResource
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-serverless-cache-tags-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
resourceArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceName
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElastiCache::ServerlessCache",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<resourceArn>\" | split(\":\") | .[-1]",
"action": "\"upsert\""
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Serverless cache
Elasticache cluster
In this step-by-step example, you will export your Cache clusters to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
Cache cluster - will represent cache clusters from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
Cache cluster blueprint
{
"identifier": "elasticache_cluster",
"title": "Elasticache Cluster",
"icon": "Service",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"engine": {
"title": "Engine",
"type": "string"
},
"engineVersion": {
"title": "Engine Version",
"type": "string"
},
"preferredAvailabilityZone": {
"title": "Preferred Availability Zone",
"type": "string"
},
"createdDate": {
"title": "Created Date",
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
},
"arn": {
"title": "ARN",
"type": "string"
},
"transitEncryptionEnabled": {
"title": "Transit Encryption Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"atRestEncryptionEnabled": {
"title": "At Rest Encryption Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"nodeType": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"title": "Node Type",
"type": "string"
},
"status": {
"title": "Cache Cluster Status",
"type": "string"
},
"numNodes": {
"title": "Num Nodes",
"type": "number"
},
"securityGroups": {
"title": "Security Groups",
"type": "array"
},
"subnetGroupName": {
"title": "Subnet Group Name",
"type": "string"
},
"link": {
"title": "Link",
"type": "string",
"format": "url"
},
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "array"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"region": {
"title": "Region",
"target": "region",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::ElastiCache::CacheCluster",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".CacheClusterId",
"title": ".CacheClusterId",
"blueprint": "aws_cache_cluster",
"properties": {
"engine": ".Engine",
"engineVersion": ".EngineVersion",
"preferredAvailabilityZone": ".PreferredAvailabilityZone",
"createdDate": ".CacheClusterCreateTime",
"arn": ".ARN",
"transitEncryptionEnabled": ".TransitEncryptionEnabled",
"atRestEncryptionEnabled": ".AtRestEncryptionEnabled",
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .ARN",
"nodeType": ".CacheNodeType",
"status": ".CacheClusterStatus",
"tags": ".Tags",
"numNodes": ".NumCacheNodes",
"securityGroups": ".CacheSecurityGroups",
"subnetGroupName": ".CacheSubnetGroupName"
},
"relations": {
"region": ".ARN | split(\":\") | .[3]"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"elasticache:DescribeCacheClusters",
"elasticache:ListTagsForResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in Elasticache clusters.
You may use the following CloudFormation template:
Event rule CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
ElasticacheEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.elasticache
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticache.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateCacheCluster
- prefix: DeleteCacheCluster
- prefix: ModifyCacheCluster
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-cache-cluster-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
cacheName: $.detail.responseElements.cacheClusterId
InputTemplate: >-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElastiCache::CacheCluster",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<cacheName>\"",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | startswith(\"DeleteCacheCluster\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
ElasticacheTagRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.elasticache
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- elasticache.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: AddTagsToResource
- prefix: RemoveTagsFromResource
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-cache-cluster-tags-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
resourceArn: $.detail.requestParameters.resourceName
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::ElastiCache::CacheCluster",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<resourceArn>\" | split(\":\") | .[-1]",
"action": "\"upsert\""
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Cache clusters
Auto scaling group
In this step-by-step example, you will export your EC2 Auto scaling groups to Port.
-
Create the following Port blueprint:
Auto scaling group - will represent EC2 auto scaling group from the AWS account.
You may use the following definitions:
Auto scaling group blueprint
{
"identifier": "awsAutoScalingGroup",
"title": "Auto Scaling Group",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"availabilityZones": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Availability Zones"
},
"desiredCapacity": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Desired Capacity"
},
"healthCheckType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Health Check Type"
},
"loadBalancerNames": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Load Balancer Names"
},
"maximumCapacity": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Maximum Capacity"
},
"minimumCapacity": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Minimum Capacity"
},
"serviceRoleArn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Service Role ARN"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"region": {
"title": "Region",
"target": "region",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Upload the
config.jsonfile to the exporter's S3 bucket:Port AWS exporter config.json
{
"resources": [
{
"kind": "AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".AutoScalingGroupName",
"title": ".AutoScalingGroupName",
"blueprint": "awsAutoScalingGroup",
"properties": {
"tags": ".Tags",
"desiredCapacity": ".DesiredCapacity",
"minimumCapacity": ".MinSize",
"maximumCapacity": ".MaxSize",
"availabilityZones": ".AvailabilityZones",
"loadBalancerNames": ".LoadBalancerNames",
"serviceRoleArn": ".ServiceLinkedRoleARN",
"healthCheckType": ".HealthCheckType"
},
"relations": {}
}
]
}
}
}
]
} -
Update the exporter's
IAM policy:IAM policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["autoscaling:Describe*"],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
} -
Optional: create an event rule to trigger automatic syncing of changes in Auto scaling groups.
You may use the following CloudFormation template:
Event rule CloudFormation template
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: The template used to create event rules for the Port AWS exporter.
Parameters:
PortAWSExporterStackName:
Description: Name of the Port AWS exporter stack name
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: ^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$
Default: serverlessrepo-port-aws-exporter
Resources:
AutoScalingGroupEventRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
source:
- aws.autoscaling
detail:
eventSource:
- autoscaling.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateAutoScalingGroup
- prefix: DeleteAutoScalingGroup
- prefix: UpdateAutoScalingGroup
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-auto-scaling-group-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
autoScalingGroupName: $.detail.requestParameters.autoScalingGroupName
InputTemplate: >-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<autoScalingGroupName>\"",
"action": "if \"<eventName>\" | startswith(\"DeleteAutoScalingGroup\") then \"delete\" else \"upsert\" end"
}
AutoScalingGroupTagRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
EventBusName: default
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.autoscaling
detail-type:
- AWS API Call via CloudTrail
detail:
eventSource:
- autoscaling.amazonaws.com
eventName:
- prefix: CreateOrUpdateTags
- prefix: DeleteTags
Name: port-aws-exporter-sync-auto-scaling-group-tags-trails
State: ENABLED
Targets:
- Id: PortAWSExporterEventsQueue
Arn:
Fn::ImportValue:
Fn::Sub: ${PortAWSExporterStackName}-EventsQueueARN
InputTransformer:
InputPathsMap:
awsRegion: $.detail.awsRegion
eventName: $.detail.eventName
resourceId: $.detail.requestParameters.tags[0].resourceId
InputTemplate: |-
{
"resource_type": "AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup",
"region": "\"<awsRegion>\"",
"identifier": "\"<resourceId>\"",
"action": "\"upsert\""
}
Done! soon, you will be able to see any Auto scaling groups
Connect Cloud Resources to Services.
This guide demonstrates how to connect a Cloud Resource to a service or list of services by relying on the tags property and using JQ mapping. We will be using an S3 bucket as the Cloud Resource.
This guide assumes that you have ingested S3 buckets into Port using the terraform option of the AWS exporter.
Ingest Services from GitHub.
Follow this guide to ingest your GitHub repositories into Port. Port will create a service blueprint that you will be using subsequently.
Service Blueprint
{
"identifier": "service",
"title": "Service",
"icon": "Github",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"readme": {
"title": "README",
"type": "string",
"format": "markdown",
"icon": "Book"
},
"url": {
"title": "URL",
"format": "url",
"type": "string",
"icon": "Link"
},
"language": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Language",
"icon": "Git"
},
"slack": {
"icon": "Slack",
"type": "string",
"title": "Slack",
"format": "url"
},
"tier": {
"title": "Tier",
"type": "string",
"description": "How mission-critical the service is",
"enum": [
"Mission Critical",
"Customer Facing",
"Internal Service",
"Other"
],
"enumColors": {
"Mission Critical": "turquoise",
"Customer Facing": "green",
"Internal Service": "darkGray",
"Other": "yellow"
},
"icon": "DefaultProperty"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Your data model should now contain the Service blueprint:
Create the relation
Now that Port is synced with your s3_bucket and service blueprints, let's map the two together.
- Add a tag to the bucket with the key
serviceand a value representing the identifier of the service. For instance, if your service has an identifier ofwebapp, create a tag on the bucket with{ "service": "webapp" }.
Refer to this AWS guide for more details on tagging resources in S3.
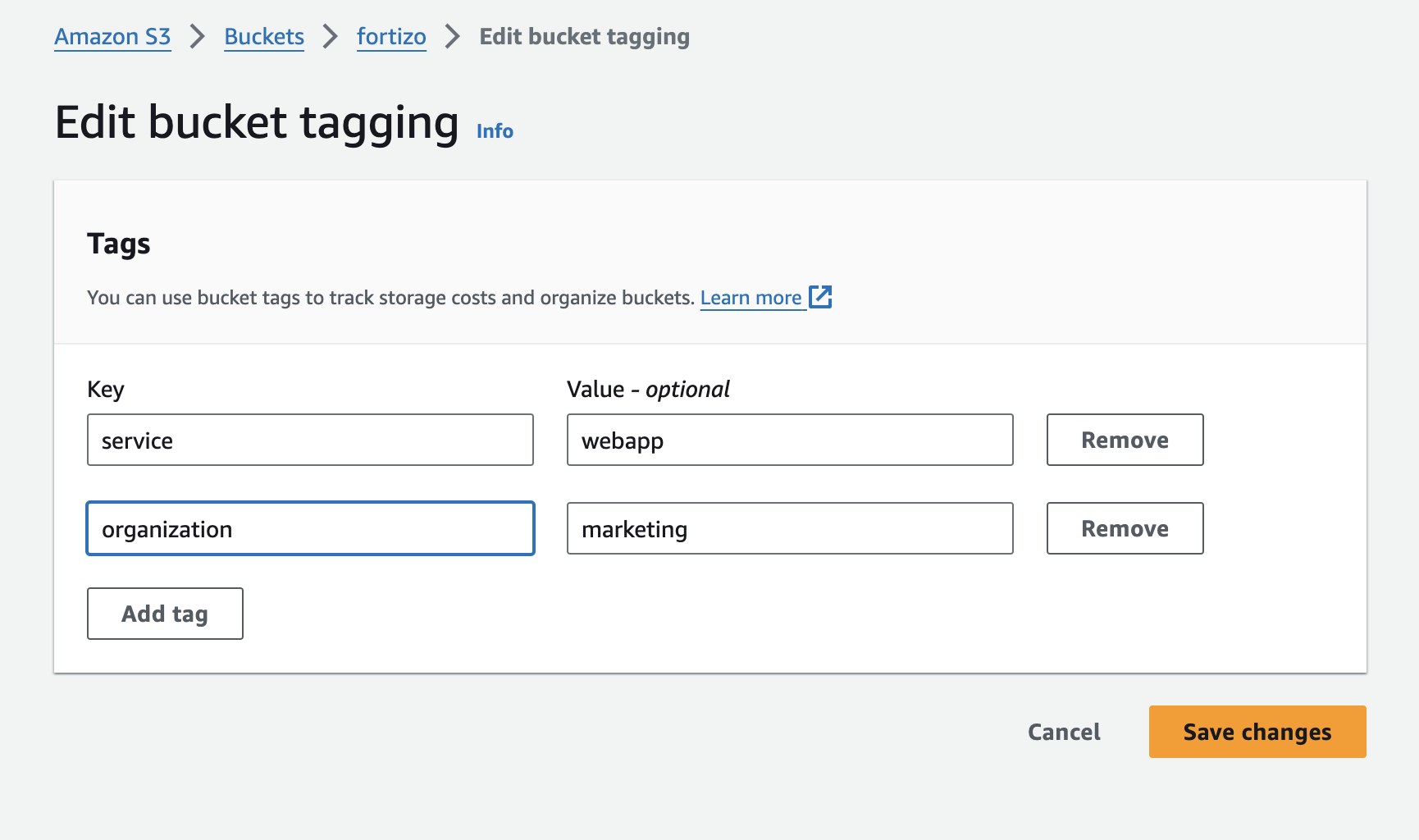
- In the Port AWS exporter repository you cloned during the ingestion step, go to the
template-assets/aws/s3_bucketfolder. We are going to add a relation from our S3 bucket configuration to theServiceblueprint by editing two files:blueprint.tf: We will define the relation toservicein the S3 bucket blueprint.config.json: We then write the mapping logic to define how a service is linked to a bucket based on tags.
S3 Bucket Blueprint
terraform {
required_providers {
port-labs = {
source = "port-labs/port-labs"
version = "2.0.3"
}
}
}
resource "port-labs_blueprint" "s3_bucket" {
title = "S3 Bucket"
icon = "Bucket"
identifier = "s3_bucket"
// ... other properties
properties {
identifier = "tags"
type = "array"
title = "Tags"
}
relations {
target = "service"
title = "Consuming Service"
identifier = "consumingService"
many = false
required = false
}
}
Mapping Logic
{
"kind": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"port": {
"entity": {
"mappings": [
{
"identifier": ".BucketName",
"title": ".BucketName",
"blueprint": "s3_bucket",
"properties": {
"link": "\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=\" + .Arn",
"regionalDomainName": ".RegionalDomainName",
"versioningStatus": ".VersioningConfiguration.Status",
"encryption": ".BucketEncryption.ServerSideEncryptionConfiguration",
"lifecycleRules": ".LifecycleConfiguration.Rules",
"publicAccess": ".PublicAccessBlockConfiguration",
"tags": ".Tags",
"arn": ".Arn"
},
"relations": {
"consumingService": ".Tags[] | select(.Key == \"service\") | .Value"
}
}
]
}
}
}
- Run terraform again to apply the changes
# Run the aws exporter again.
terraform apply -var 'resources=["s3_bucket"]'
View the relation
You can view the relation in your data model
Now go to your catalog, and click on the S3 bucket you used in this guide. You will see it connected to the service.
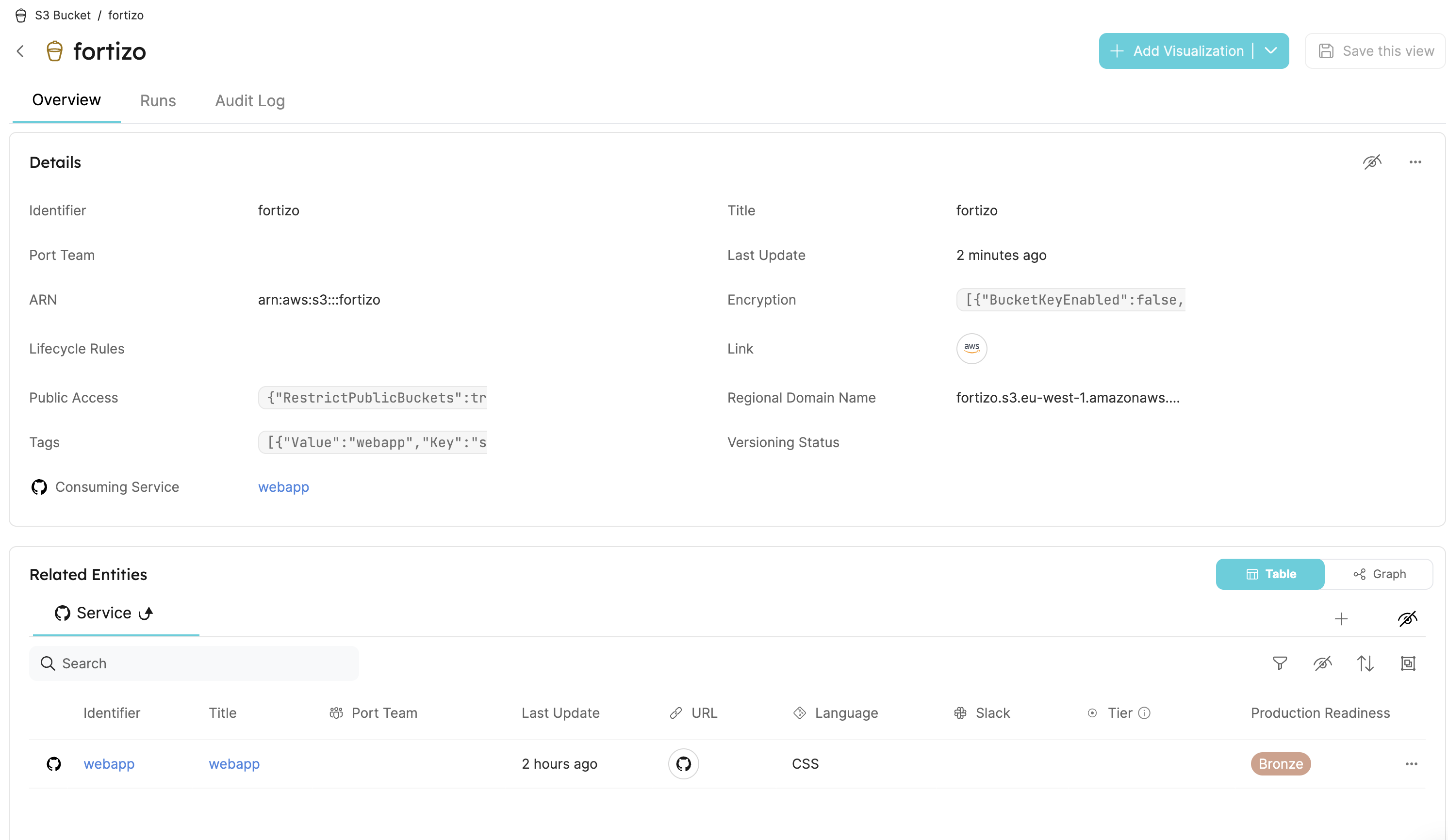
Done! 🎉 You can replicate this for all your other resources.