OpenCost
Port's Opencost integration allows you to model Opencost resources in your software catalog and ingest data into them.
Overview
This integration allows you to:
- Map and organize your desired Opencost resources and their metadata in Port (see supported resources below).
- Watch for Opencost object changes (create/update/delete) in real-time, and automatically apply the changes to your entities in Port.
Supported Resources
The resources that can be ingested from Opencost into Port are listed below. It is possible to reference any field that appears in the API responses linked below in the mapping configuration.
Setup
Choose one of the following installation methods:
- Real-time (self-hosted)
- Scheduled (CI)
Using this installation option means that the integration will be able to update Port in real time using webhooks.
Prerequisites
To install the integration, you need a Kubernetes cluster that the integration's container chart will be deployed to.
Please make sure that you have kubectl and helm installed on your machine, and that your kubectl CLI is connected to the Kubernetes cluster where you plan to install the integration.
If you are having trouble installing this integration, please refer to these troubleshooting steps.
For details about the available parameters for the installation, see the table below.
- Helm
- ArgoCD
To install the integration using Helm:
-
Go to the Opencost data source page in your portal.
-
Select the
Real-time and always onmethod:
-
A
helmcommand will be displayed, with default values already filled out (e.g. your Port cliend ID, client secret, etc).
Copy the command, replace the placeholders with your values, then run it in your terminal to install the integration.
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
To install the integration using ArgoCD:
- Create a
values.yamlfile inargocd/my-ocean-opencost-integrationin your git repository with the content:
Remember to replace the placeholders for OPENCOST_HOST.
initializePortResources: true
scheduledResyncInterval: 120
integration:
identifier: my-ocean-opencost-integration
type: opencost
eventListener:
type: POLLING
config:
opencostHost: OPENCOST_HOST
- Install the
my-ocean-opencost-integrationArgoCD Application by creating the followingmy-ocean-opencost-integration.yamlmanifest:
Remember to replace the placeholders for YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_ID YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET and YOUR_GIT_REPO_URL.
Multiple sources ArgoCD documentation can be found here.
ArgoCD Application
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-ocean-opencost-integration
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: my-ocean-opencost-integration
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
sources:
- repoURL: 'https://port-labs.github.io/helm-charts/'
chart: port-ocean
targetRevision: 0.1.14
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/argocd/my-ocean-opencost-integration/values.yaml
parameters:
- name: port.clientId
value: YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_ID
- name: port.clientSecret
value: YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET
- name: port.baseUrl
value: https://api.getport.io
- repoURL: YOUR_GIT_REPO_URL
targetRevision: main
ref: values
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
- Apply your application manifest with
kubectl:
kubectl apply -f my-ocean-opencost-integration.yaml
This table summarizes the available parameters for the installation.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
port.clientId | Your port client id | ✅ |
port.clientSecret | Your port client secret | ✅ |
port.baseUrl | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
integration.identifier | Change the identifier to describe your integration | ✅ |
integration.type | The integration type | ✅ |
integration.eventListener.type | The event listener type | ✅ |
integration.config.opencostHost | The Opencost server URL | ✅ |
scheduledResyncInterval | The number of minutes between each resync | ❌ |
initializePortResources | Default true, When set to true the integration will create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
sendRawDataExamples | Enable sending raw data examples from the third party API to port for testing and managing the integration mapping. Default is true | ❌ |
This workflow/pipeline will run the Opencost integration once and then exit, this is useful for scheduled ingestion of data.
If you want the integration to update Port in real time you should use the Real-time (self-hosted) installation option
- GitHub
- Jenkins
- Azure Devops
- GitLab
Make sure to configure the following Github Secrets:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST | The Opencost server URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__SEND_RAW_DATA_EXAMPLES | Enable sending raw data examples from the third party API to port for testing and managing the integration mapping. Default is true | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for opencost-integration.yml workflow file:
name: Opencost Exporter Workflow
on:
workflow_dispatch:
schedule:
- cron: '0 */1 * * *' # Determines the scheduled interval for this workflow. This example runs every hour.
jobs:
run-integration:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
timeout-minutes: 30 # Set a time limit for the job
steps:
- uses: port-labs/ocean-sail@v1
with:
type: 'opencost'
port_client_id: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID }}
port_client_secret: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET }}
port_base_url: https://api.getport.io
config: |
opencost_host: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST }}
Your Jenkins agent should be able to run docker commands.
Make sure to configure the following Jenkins Credentials
of Secret Text type:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST | The Opencost server URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__SEND_RAW_DATA_EXAMPLES | Enable sending raw data examples from the third party API to port for testing and managing the integration mapping. Default is true | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for Jenkinsfile groovy pipeline file:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Run Opencost Integration') {
steps {
script {
withCredentials([
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST', variable: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID', variable: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET', variable: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET'),
]) {
sh('''
#Set Docker image and run the container
integration_type="opencost"
version="latest"
image_name="ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-${integration_type}:${version}"
docker run -i --rm --platform=linux/amd64 \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__SEND_RAW_DATA_EXAMPLES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$image_name
exit $?
''')
}
}
}
}
}
}
Your Azure Devops agent should be able to run docker commands. Learn more about agents here.
Variable groups store values and secrets you'll use in your pipelines across your project. Learn more
Setting Up Your Credentials
- Create a Variable Group: Name it port-ocean-credentials.
- Store the required variables (see the table below).
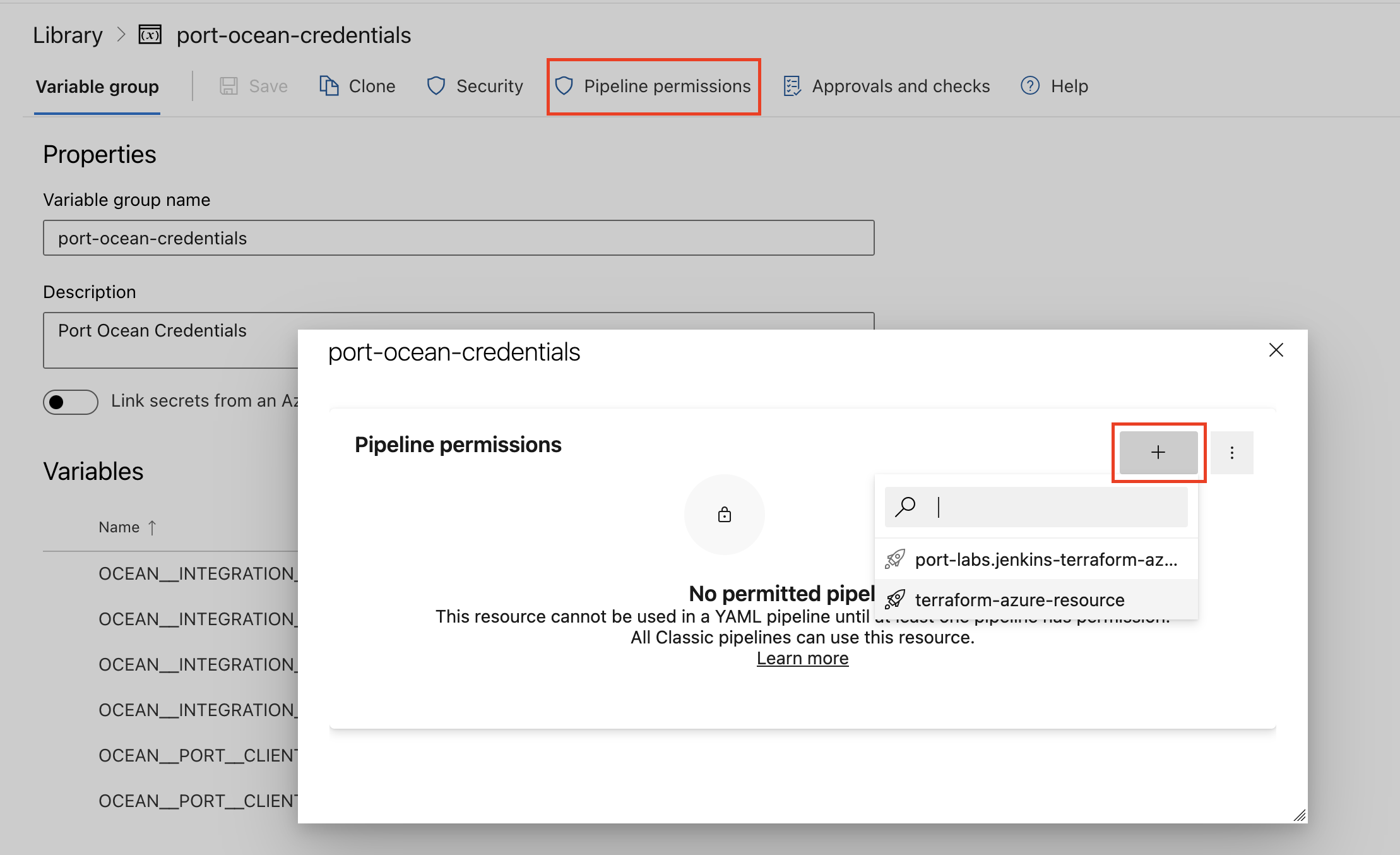
- Authorize Your Pipeline:
- Go to "Library" -> "Variable groups."
- Find port-ocean-credentials and click on it.
- Select "Pipeline Permissions" and add your pipeline to the authorized list.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST | The Opencost server URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__SEND_RAW_DATA_EXAMPLES | Enable sending raw data examples from the third party API to port for testing and managing the integration mapping. Default is true | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for opencost-integration.yml pipeline file:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: "ubuntu-latest"
variables:
- group: port-ocean-credentials
steps:
- script: |
# Set Docker image and run the container
integration_type="opencost"
version="latest"
image_name="ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-$integration_type:$version"
docker run -i --rm \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__SEND_RAW_DATA_EXAMPLES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST=$(OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$(OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$(OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$image_name
exit $?
displayName: 'Ingest Data into Port'
Make sure to configure the following GitLab variables:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST | The Opencost server URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__SEND_RAW_DATA_EXAMPLES | Enable sending raw data examples from the third party API to port for testing and managing the integration mapping. Default is true | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (How to get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for .gitlab-ci.yml pipeline file:
default:
image: docker:24.0.5
services:
- docker:24.0.5-dind
before_script:
- docker info
variables:
INTEGRATION_TYPE: opencost
VERSION: latest
stages:
- ingest
ingest_data:
stage: ingest
variables:
IMAGE_NAME: ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-$INTEGRATION_TYPE:$VERSION
script:
- |
docker run -i --rm --platform=linux/amd64 \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__SEND_RAW_DATA_EXAMPLES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__OPENCOST_HOST \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$IMAGE_NAME
rules: # Run only when changes are made to the main branch
- if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "main"'
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
For advanced configuration such as proxies or self-signed certificates, click here.
Configuration
Port integrations use a YAML mapping block to ingest data from the third-party api into Port.
The mapping makes use of the JQ JSON processor to select, modify, concatenate, transform and perform other operations on existing fields and values from the integration API.
Examples
Examples of blueprints and the relevant integration configurations:
Cost
Cost blueprint
{
"identifier": "openCostResourceAllocation",
"description": "This blueprint represents an OpenCost resource allocation in our software catalog",
"title": "OpenCost Resource Allocation",
"icon": "Cluster",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"cluster": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Cluster"
},
"namespace": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Namespace"
},
"startDate": {
"title": "Start Date",
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
},
"endDate": {
"title": "End Date",
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
},
"cpuCoreHours": {
"title": "CPU Core Hours",
"type": "number"
},
"cpuCost": {
"title": "CPU Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"cpuEfficiency": {
"title": "CPU Efficiency",
"type": "number"
},
"gpuHours": {
"title": "GPU Hours",
"type": "number"
},
"gpuCost": {
"title": "GPU Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"networkCost": {
"title": "Network Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"loadBalancerCost": {
"title": "Load Balancer Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"pvCost": {
"title": "PV Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"ramBytes": {
"title": "RAM Bytes",
"type": "number"
},
"ramCost": {
"title": "RAM Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"ramEfficiency": {
"title": "RAM Efficiency",
"type": "number"
},
"sharedCost": {
"title": "Shared Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"externalCost": {
"title": "External Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"totalCost": {
"title": "Total Cost",
"type": "number"
},
"totalEfficiency": {
"title": "Total Efficiency",
"type": "number"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Integration configuration
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: cost
selector:
query: "true"
window: "month"
aggregate: "pod"
step: "window"
resolution: "1m"
filter: 'labels:"app:internal-service","app:service-2"+service:"notification","account","functions"'
port:
entity:
mappings:
blueprint: '"openCostResourceAllocation"'
identifier: .name
title: .name
properties:
cluster: .properties.cluster
namespace: .properties.namespace
startDate: .start
endDate: .end
cpuCoreHours: .cpuCoreHours
cpuCost: .cpuCost
cpuEfficiency: .cpuEfficiency
gpuHours: .gpuHours
gpuCost: .gpuCost
networkCost: .networkCost
loadBalancerCost: .loadBalancerCost
pvCost: .pvCost
ramBytes: .ramBytes
ramCost: .ramCost
ramEfficiency: .ramEfficiency
sharedCost: .sharedCost
externalCost: .externalCost
totalCost: .totalCost
totalEfficiency: .totalEfficiency
Let's Test It
This section includes a sample response data from OpenCost. In addition, it includes the entity created from the resync event based on the Ocean configuration provided in the previous section.
Payload
Here is an example of the payload structure from OpenCost aggregated on the namespace level:
Cost response data
{
"name": "ingress-nginx",
"properties": {
"cluster": "cluster-one",
"node": "minikube",
"container": "controller",
"controller": "ingress-nginx-controller",
"controllerKind": "deployment",
"namespace": "ingress-nginx",
"pod": "ingress-nginx-controller-7799c6795f-29n7j",
"services": [
"ingress-nginx-controller-admission",
"ingress-nginx-controller"
],
"labels": {
"app_kubernetes_io_component": "controller",
"app_kubernetes_io_instance": "ingress-nginx",
"app_kubernetes_io_name": "ingress-nginx",
"gcp_auth_skip_secret": "true",
"kubernetes_io_metadata_name": "ingress-nginx",
"pod_template_hash": "7799c6795f"
},
"namespaceLabels": {
"app_kubernetes_io_instance": "ingress-nginx",
"app_kubernetes_io_name": "ingress-nginx",
"kubernetes_io_metadata_name": "ingress-nginx"
}
},
"window": {
"start": "2023-10-30T00:00:00Z",
"end": "2023-10-31T00:00:00Z"
},
"start": "2023-10-30T09:05:00Z",
"end": "2023-10-30T11:50:00Z",
"minutes": 165,
"cpuCores": 0.1,
"cpuCoreRequestAverage": 0.1,
"cpuCoreUsageAverage": 0,
"cpuCoreHours": 0.275,
"cpuCost": 0.00869,
"cpuCostAdjustment": 0,
"cpuEfficiency": 0,
"gpuCount": 0,
"gpuHours": 0,
"gpuCost": 0,
"gpuCostAdjustment": 0,
"networkTransferBytes": 0,
"networkReceiveBytes": 0,
"networkCost": 0,
"networkCrossZoneCost": 0,
"networkCrossRegionCost": 0,
"networkInternetCost": 0,
"networkCostAdjustment": 0,
"loadBalancerCost": 0,
"loadBalancerCostAdjustment": 0,
"pvBytes": 0,
"pvByteHours": 0,
"pvCost": 0,
"pvs": "None",
"pvCostAdjustment": 0,
"ramBytes": 94371840,
"ramByteRequestAverage": 94371840,
"ramByteUsageAverage": 0,
"ramByteHours": 259522560,
"ramCost": 0.00102,
"ramCostAdjustment": 0,
"ramEfficiency": 0,
"externalCost": 0,
"sharedCost": 0,
"totalCost": 0.00972,
"totalEfficiency": 0,
"lbAllocations": "None"
}
Mapping Result
The combination of the sample payload and the Ocean configuration generates the following Port entity:
Cost entity in Port
{
"identifier": "ingress-nginx",
"title": "ingress-nginx",
"blueprint": "openCostResourceAllocation",
"team": [],
"properties": {
"cluster": "cluster-one",
"namespace": "ingress-nginx",
"startDate": "2023-10-30T09:05:00.000Z",
"endDate": "2023-10-30T11:50:00.000Z",
"cpuCoreHours": 0.275,
"cpuCost": 0.00869,
"cpuEfficiency": 0,
"gpuHours": 0,
"gpuCost": 0,
"networkCost": 0,
"loadBalancerCost": 0,
"pvCost": 0,
"ramBytes": 94371840,
"ramCost": 0.00102,
"ramEfficiency": 0,
"sharedCost": 0,
"externalCost": 0,
"totalCost": 0.00972,
"totalEfficiency": 0
},
"relations": {},
"createdAt": "2023-10-15T09:30:57.924Z",
"createdBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW",
"updatedAt": "2023-10-30T11:49:20.881Z",
"updatedBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW"
}