Dynatrace
Port's Dynatrace integration allows you to model Dynatrace resources in your software catalog and ingest data into them.
Overview
This integration allows you to:
- Map and organize your desired Dynatrace resources and their metadata in Port (see supported resources below).
- Watch for Dynatrace object changes (create/update/delete) in real-time, and automatically apply the changes to your software catalog.
Supported Resources
The resources that can be ingested from Dynatrace into Port are listed below. It is possible to reference any field that appears in the API responses linked below for the mapping configuration.
problementitysloentity typesfor selectors in theentityresource.
Prerequisites
Generate a Dynatrace API key
- Navigate to
<instanceURL>/ui/apps/dynatrace.classic.tokens/ui/access-tokens. For example, if you access your Dynatrace instance athttps://npm82883.apps.dynatrace.com, you should navigate tohttps://npm82883.apps.dynatrace.com/ui/apps/dynatrace.classic.tokens/ui/access-tokens. - Click Generate new token to create a new token. Ensure the permissions:
DataExport,Read entities,Read problemsandRead SLOare assigned to the token. TheDataExportpermission allows Dynatrace to perform healthchecks before ingestion starts.
Construct your Dynatrace Host URL
Your Dynatrace host URL should be https://<environment-id>.live.dynatrace.com. Note that there is a difference between the instance URL and the API host URL. The former contains apps while the latter (as shown prior) uses live. This means if your environment ID is npm82883, your API host URL should be https://npm82883.live.dynatrace.com.
Setup
Choose one of the following installation methods:
- Hosted by Port
- Real-time (self-hosted)
- Scheduled (CI)
Using this installation option means that the integration will be hosted by Port, with a customizable resync interval to ingest data into Port.
Live event support
Currently, live events are not supported for integrations hosted by Port.
Resyncs will be performed periodically (with a configurable interval), or manually triggered by you via Port's UI.
Therefore, real-time events (including GitOps) will not be ingested into Port immediately.
Support for live events is WIP and will be supported in the near future.
Alternatively, you can install the integration using the Real-time (self-hosted) method to update Port in real time using webhooks.
Installation
To install, follow these steps:
-
Go to the Data sources page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ Data sourcebutton in the top-right corner. -
Click on the relevant integration in the list.
-
Under
Select your installation method, chooseHosted by Port. -
Configure the
integration settingsandapplication settingsas you wish (see below for details).
Application settings
Every integration hosted by Port has the following customizable application settings, which are configurable after installation:
-
Resync interval: The frequency at which Port will ingest data from the integration. There are various options available, ranging from every 1 hour to once a day. -
Send raw data examples: A boolean toggle (enabledby default). If enabled, raw data examples will be sent from the integration to Port. These examples are used when testing your mapping configuration, they allow you to run yourjqexpressions against real data and see the results.
Integration settings
Every integration has its own tool-specific settings, under the Integration settings section.
Each of these settings has an ⓘ icon next to it, which you can hover over to see a description of the setting.
Port secrets
Some integration settings require sensitive pieces of data, such as tokens.
For these settings, Port secrets will be used, ensuring that your sensitive data is encrypted and secure.
When filling in such a setting, its value will be obscured (shown as ••••••••).
For each such setting, Port will automatically create a secret in your organization.
To see all secrets in your organization, follow these steps.
Port source IP addresses
When using this installation method, Port will make outbound calls to your 3rd-party applications from static IP addresses.
You may need to add these addresses to your allowlist, in order to allow Port to interact with the integrated service:
- Europe (EU)
- United States (US)
54.73.167.226
63.33.143.237
54.76.185.219
3.234.37.33
54.225.172.136
3.225.234.99
Using this installation option means that the integration will be able to update Port in real time using webhooks.
Prerequisites
To install the integration, you need a Kubernetes cluster that the integration's container chart will be deployed to.
Please make sure that you have kubectl and helm installed on your machine, and that your kubectl CLI is connected to the Kubernetes cluster where you plan to install the integration.
If you are having trouble installing this integration, please refer to these troubleshooting steps.
For details about the available parameters for the installation, see the table below.
- Helm
- ArgoCD
To install the integration using Helm:
-
Go to the Dynatrace data source page in your portal.
-
Select the
Real-time and always onmethod:
-
A
helmcommand will be displayed, with default values already filled out (e.g. your Port cliend ID, client secret, etc).
Copy the command, replace the placeholders with your values, then run it in your terminal to install the integration.
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
To install the integration using ArgoCD:
- Create a
values.yamlfile inargocd/my-ocean-dynatrace-integrationin your git repository with the content:
Remember to replace the placeholders for DYNATRACE_HOST_URL and DYNATRACE_API_KEY.
initializePortResources: true
scheduledResyncInterval: 120
integration:
identifier: my-ocean-dynatrace-integration
type: dynatrace
eventListener:
type: POLLING
config:
dynatraceHostUrl: DYNATRACE_HOST_URL
secrets:
dynatraceApiKey: DYNATRACE_API_KEY
- Install the
my-ocean-dynatrace-integrationArgoCD Application by creating the followingmy-ocean-dynatrace-integration.yamlmanifest:
Remember to replace the placeholders for YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_ID YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET and YOUR_GIT_REPO_URL.
Multiple sources ArgoCD documentation can be found here.
ArgoCD Application
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-ocean-dynatrace-integration
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: my-ocean-dynatrace-integration
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
sources:
- repoURL: 'https://port-labs.github.io/helm-charts/'
chart: port-ocean
targetRevision: 0.1.14
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/argocd/my-ocean-dynatrace-integration/values.yaml
parameters:
- name: port.clientId
value: YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_ID
- name: port.clientSecret
value: YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET
- name: port.baseUrl
value: https://api.getport.io
- repoURL: YOUR_GIT_REPO_URL
targetRevision: main
ref: values
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
- Apply your application manifest with
kubectl:
kubectl apply -f my-ocean-dynatrace-integration.yaml
This table summarizes the available parameters for the installation.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
port.clientId | Your port client id | ✅ |
port.clientSecret | Your port client secret | ✅ |
port.baseUrl | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
integration.identifier | Change the identifier to describe your integration | ✅ |
integration.type | The integration type | ✅ |
integration.eventListener.type | The event listener type | ✅ |
integration.secrets.dynatraceApiKey | API Key for Dynatrace instance, docs can be found here | ✅ |
integration.config.dynatraceHostUrl | The API URL of the Dynatrace instance | ✅ |
scheduledResyncInterval | The number of minutes between each resync | ❌ |
initializePortResources | Default true, When set to true the integration will create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
This workflow/pipeline will run the Dynatrace integration once and then exit, this is useful for scheduled ingestion of data.
If you want the integration to update Port in real time using webhooks, use the Real-time (self-hosted) installation option.
- GitHub
- Jenkins
- Azure Devops
- GitLab
Make sure to configure the following Github Secrets:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY | The Dynatrace API key , docs can be found here | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL | The Dynatrace API host URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for dynatrace-integration.yml workflow file:
name: Dynatrace Exporter Workflow
on:
workflow_dispatch:
schedule:
- cron: '0 */1 * * *' # Determines the scheduled interval for this workflow. This example runs every hour.
jobs:
run-integration:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
timeout-minutes: 30 # Set a time limit for the job
steps:
- uses: port-labs/ocean-sail@v1
with:
type: 'dynatrace'
port_client_id: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID }}
port_client_secret: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET }}
port_base_url: https://api.getport.io
config: |
dynatrace_api_key: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY }}
dynatrace_host_url: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL }}
Your Jenkins agent should be able to run docker commands.
Make sure to configure the following Jenkins Credentials
of Secret Text type:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY | The Dynatrace API key | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL | The Dynatrace host URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for Jenkinsfile groovy pipeline file:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Run Dynatrace Integration') {
steps {
script {
withCredentials([
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY', variable: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL', variable: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID', variable: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET', variable: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET'),
]) {
sh('''
#Set Docker image and run the container
integration_type="dynatrace"
version="latest"
image_name="ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-${integration_type}:${version}"
docker run -i --rm --platform=linux/amd64 \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$image_name
exit $?
''')
}
}
}
}
}
}
Your Azure Devops agent should be able to run docker commands. Learn more about agents here.
Variable groups store values and secrets you'll use in your pipelines across your project. Learn more
Setting Up Your Credentials
- Create a Variable Group: Name it port-ocean-credentials.
- Store the required variables (see the table below).
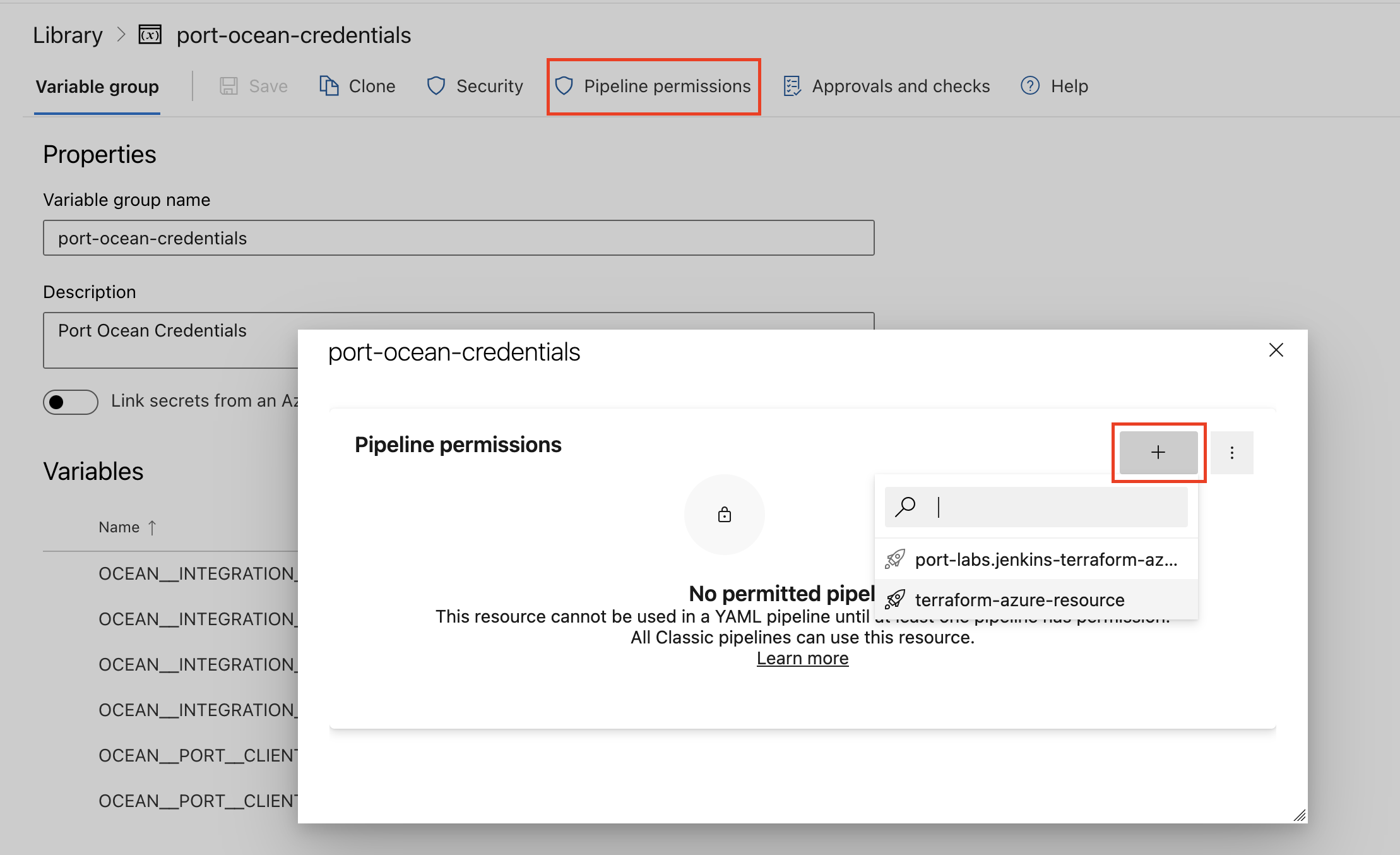
- Authorize Your Pipeline:
- Go to "Library" -> "Variable groups."
- Find port-ocean-credentials and click on it.
- Select "Pipeline Permissions" and add your pipeline to the authorized list.
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY | The Dynatrace API key | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL | The Dynatrace API host URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for dyntrace-integration.yml pipeline file:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: "ubuntu-latest"
variables:
- group: port-ocean-credentials
steps:
- script: |
# Set Docker image and run the container
integration_type="dynatrace"
version="latest"
image_name="ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-$integration_type:$version"
docker run -i --rm \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY=$(OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY) \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL=$(OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$(OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$(OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$image_name
exit $?
displayName: 'Ingest Data into Port'
Make sure to configure the following GitLab variables:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY | The Dynatrace API key | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL | The Dynatrace API host URL | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Change the identifier to describe your integration, if not set will use the default one | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for .gitlab-ci.yml pipeline file:
default:
image: docker:24.0.5
services:
- docker:24.0.5-dind
before_script:
- docker info
variables:
INTEGRATION_TYPE: dynatrace
VERSION: latest
stages:
- ingest
ingest_data:
stage: ingest
variables:
IMAGE_NAME: ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-$INTEGRATION_TYPE:$VERSION
script:
- |
docker run -i --rm --platform=linux/amd64 \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_API_KEY \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__DYNATRACE_HOST_URL \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$IMAGE_NAME
rules: # Run only when changes are made to the main branch
- if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "main"'
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port (https://app.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.getport.io. - If you use the US region of Port (https://app.us.getport.io), your API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io.
Configuration
Port integrations use a YAML mapping block to ingest data from the third-party api into Port.
The mapping makes use of the JQ JSON processor to select, modify, concatenate, transform and perform other operations on existing fields and values from the integration API.
Ingest additional resource types
By default, the entity kind ingests only entities of type APPLICATION and SERVICE due to the large number of available resources. However, you can configure the entity kind mapping to ingest entities of other types.
To do this, use the entityTypes selector in the entity mapping like so:
Mapping configuration (Click to expand)
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: entity
selector:
query: "true"
entityTypes: ["APPLICATION", "SERVICE"]
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .entityId
title: .displayName
blueprint: '"dynatraceEntity"'
properties:
firstSeen: ".firstSeenTms / 1000 | todate"
lastSeen: ".lastSeenTms / 1000 | todate"
type: .type
tags: .tags[].stringRepresentation
managementZones: .managementZones[].name
properties: .properties
fromRelationships: .fromRelationships
toRelationships: .toRelationships
Available resource types�
You can retrieve a list of available resource types by using the Dynatrace Entity Types API. Below is a list of resource types retrieved from the API:
Dynatrace entity types (Click to expand)
APM_SECURITY_GATEWAYAPPLICATIONAPPLICATION_METHODAPPLICATION_METHOD_GROUPAPPMON_SERVERAPPMON_SYSTEM_PROFILEAUTO_SCALING_GROUPAWS_APPLICATION_LOAD_BALANCERAWS_AVAILABILITY_ZONEAWS_CREDENTIALSAWS_LAMBDA_FUNCTIONAWS_NETWORK_LOAD_BALANCERAZURE_API_MANAGEMENT_SERVICEAZURE_APPLICATION_GATEWAYAZURE_APP_SERVICE_PLANAZURE_COSMOS_DBAZURE_CREDENTIALSAZURE_EVENT_HUBAZURE_EVENT_HUB_NAMESPACEAZURE_FUNCTION_APPAZURE_IOT_HUBAZURE_LOAD_BALANCERAZURE_MGMT_GROUPAZURE_REDIS_CACHEAZURE_REGIONAZURE_SERVICE_BUS_NAMESPACEAZURE_SERVICE_BUS_QUEUEAZURE_SERVICE_BUS_TOPICAZURE_SQL_DATABASEAZURE_SQL_ELASTIC_POOLAZURE_SQL_SERVERAZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNTAZURE_SUBSCRIPTIONAZURE_TENANTAZURE_VMAZURE_VM_SCALE_SETAZURE_WEB_APPBOSH_DEPLOYMENTBROWSERCF_FOUNDATIONCINDER_VOLUMECLOUD_APPLICATIONCLOUD_APPLICATION_INSTANCECLOUD_APPLICATION_NAMESPACECONTAINER_GROUPCONTAINER_GROUP_INSTANCECUSTOM_APPLICATIONCUSTOM_DEVICECUSTOM_DEVICE_GROUPDATASTOREDCRUM_APPLICATIONDCRUM_SERVICEDCRUM_SERVICE_INSTANCEDEVICE_APPLICATION_METHODDEVICE_APPLICATION_METHOD_GROUPDISKDOCKER_CONTAINER_GROUPDOCKER_CONTAINER_GROUP_INSTANCEDYNAMO_DB_TABLEEBS_VOLUMEEC2_INSTANCEELASTIC_LOAD_BALANCERENVIRONMENTEXTERNAL_SYNTHETIC_TESTEXTERNAL_SYNTHETIC_TEST_STEPGCP_ZONEGEOLOCATIONGEOLOC_SITEGOOGLE_COMPUTE_ENGINEHOSTHOST_GROUPHTTP_CHECKHTTP_CHECK_STEPHYPERVISORHYPERVISOR_CLUSTERHYPERVISOR_DISKKUBERNETES_CLUSTERKUBERNETES_NODEKUBERNETES_SERVICEMOBILE_APPLICATIONMULTIPROTOCOL_MONITORNETWORK_INTERFACENEUTRON_SUBNETOPENSTACK_AVAILABILITY_ZONEOPENSTACK_COMPUTE_NODEOPENSTACK_PROJECTOPENSTACK_REGIONOPENSTACK_VMOSPROCESS_GROUPPROCESS_GROUP_INSTANCEQUEUEQUEUE_INSTANCERELATIONAL_DATABASE_SERVICERUNTIME_COMPONENTS3BUCKETSERVICESERVICE_INSTANCESERVICE_METHODSERVICE_METHOD_GROUPSOFTWARE_COMPONENTSWIFT_CONTAINERSYNTHETIC_LOCATIONSYNTHETIC_TESTSYNTHETIC_TEST_STEPVCENTERVIRTUALMACHINEVMWARE_DATACENTERcloud:aws:acmprivatecacloud:aws:api_gatewaycloud:aws:app_runnercloud:aws:appstreamcloud:aws:appsynccloud:aws:athenacloud:aws:auroracloud:aws:autoscalingcloud:aws:billingcloud:aws:cassandracloud:aws:chatbotcloud:aws:cloud_frontcloud:aws:cloudhsmcloud:aws:cloudsearchcloud:aws:codebuildcloud:aws:cognitocloud:aws:connectcloud:aws:datasynccloud:aws:daxcloud:aws:dmscloud:aws:documentdbcloud:aws:dxconcloud:aws:dynamodbcloud:aws:ebscloud:aws:ec2_spotcloud:aws:ec2apicloud:aws:ecscloud:aws:ecs:clustercloud:aws:efscloud:aws:eks:clustercloud:aws:elasticachecloud:aws:elasticbeanstalkcloud:aws:elasticinferencecloud:aws:elastictranscodercloud:aws:emrcloud:aws:escloud:aws:eventscloud:aws:fsxcloud:aws:gameliftcloud:aws:gluecloud:aws:inspectorcloud:aws:iotcloud:aws:iot_things_graphcloud:aws:iotanalyticscloud:aws:kafkacloud:aws:kinesis:data_analyticscloud:aws:kinesis:data_firehosecloud:aws:kinesis:data_streamcloud:aws:kinesis:video_streamcloud:aws:lambdacloud:aws:lexcloud:aws:logscloud:aws:media_tailorcloud:aws:mediaconnectcloud:aws:mediaconvertcloud:aws:mediapackagelivecloud:aws:mediapackagevodcloud:aws:mqcloud:aws:nat_gatewaycloud:aws:neptunecloud:aws:opsworkscloud:aws:pollycloud:aws:qldbcloud:aws:rdscloud:aws:redshiftcloud:aws:rekognitioncloud:aws:robomakercloud:aws:route53cloud:aws:route53resolvercloud:aws:s3cloud:aws:sage_maker:batch_transform_jobcloud:aws:sage_maker:endpointcloud:aws:sage_maker:endpoint_instancecloud:aws:sage_maker:ground_truthcloud:aws:sage_maker:processing_jobcloud:aws:sage_maker:training_jobcloud:aws:servicecatalogcloud:aws:sescloud:aws:snscloud:aws:sqscloud:aws:ssm-runcommandcloud:aws:statescloud:aws:storagegatewaycloud:aws:swfcloud:aws:textractcloud:aws:transfercloud:aws:transitgatewaycloud:aws:translatecloud:aws:trustedadvisorcloud:aws:usagecloud:aws:vpncloud:aws:wafcloud:aws:wafv2cloud:aws:workmailcloud:aws:workspacescloud:azure:apimanagement:servicecloud:azure:app:containerappscloud:azure:app:managedenvironmentscloud:azure:appconfiguration:configurationstorescloud:azure:appplatform:springcloud:azure:automation:automationaccountscloud:azure:batch:accountcloud:azure:blockchain:blockchainmemberscloud:azure:cache:rediscloud:azure:cdn:cdnwebapplicationfirewallpoliciescloud:azure:cdn:profilescloud:azure:classic_storage_accountcloud:azure:classic_storage_account:blobcloud:azure:classic_storage_account:filecloud:azure:classic_storage_account:queuecloud:azure:classic_storage_account:tablecloud:azure:classic_virtual_machinecloud:azure:cognitiveservices:allinonecloud:azure:cognitiveservices:anomalydetectorcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:bingautosuggestcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:bingcustomsearchcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:bingentitysearchcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:bingsearchcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:bingspellcheckcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:computervisioncloud:azure:cognitiveservices:contentmoderatorcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:customvisionpredictioncloud:azure:cognitiveservices:customvisiontrainingcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:facecloud:azure:cognitiveservices:immersivereadercloud:azure:cognitiveservices:inkrecognizercloud:azure:cognitiveservices:luiscloud:azure:cognitiveservices:luisauthoringcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:openaicloud:azure:cognitiveservices:personalizercloud:azure:cognitiveservices:qnamakercloud:azure:cognitiveservices:speechcloud:azure:cognitiveservices:textanalyticscloud:azure:cognitiveservices:translatorcloud:azure:containerinstance:containergroupcloud:azure:containerregistry:registriescloud:azure:containerservice:managedclustercloud:azure:datafactory:v1cloud:azure:datafactory:v2cloud:azure:datalakeanalytics:accountscloud:azure:datalakestore:accountscloud:azure:datashare:accountscloud:azure:devices:iothubscloud:azure:devices:provisioningservicescloud:azure:documentdb:databaseaccounts:globalcloud:azure:documentdb:databaseaccounts:mongocloud:azure:eventgrid:domainscloud:azure:eventgrid:systemtopicscloud:azure:eventgrid:topicscloud:azure:eventhub:clusterscloud:azure:frontdoorcloud:azure:hdinsight:clustercloud:azure:hybridcompute:machinescloud:azure:insights:componentscloud:azure:iotcentral:iotappscloud:azure:keyvault:vaultscloud:azure:kusto:clusterscloud:azure:logic:integrationserviceenvironmentscloud:azure:logic:workflowscloud:azure:machinelearningservices:workspacescloud:azure:maps:accountscloud:azure:mariadb:servercloud:azure:media:mediaservicescloud:azure:media:mediaservices:streamingendpointscloud:azure:mysql:flexibleserverscloud:azure:mysql:servercloud:azure:netapp:netappaccounts:capacitypoolscloud:azure:netapp:netappaccounts:capacitypools:volumescloud:azure:network:applicationgatewayscloud:azure:network:azurefirewallscloud:azure:network:dnszonescloud:azure:network:expressroutecircuitscloud:azure:network:loadbalancers:basiccloud:azure:network:loadbalancers:gatewaycloud:azure:network:loadbalancers:standardcloud:azure:network:networkinterfacescloud:azure:network:networkwatchers:connectionmonitorscloud:azure:network:networkwatchers:connectionmonitors:previecloud:azure:network:privatednszonescloud:azure:network:publicipaddressescloud:azure:notificationhubs:namespaces:notificationhubscloud:azure:postgresql:flexibleserverscloud:azure:postgresql:servercloud:azure:postgresql:serverv2cloud:azure:powerbidedicated:capacitiescloud:azure:recoveryservices:vaultscloud:azure:relay:namespacescloud:azure:search:searchservicescloud:azure:servicefabricmesh:applicationscloud:azure:signalrservice:signalrcloud:azure:sql:managedcloud:azure:sql:serverscloud:azure:sql:servers:databases:datawarehousecloud:azure:sql:servers:databases:dtucloud:azure:sql:servers:databases:hyperscalecloud:azure:sql:servers:databases:vcorecloud:azure:sql:servers:elasticpools:dtucloud:azure:sql:servers:elasticpools:vcorecloud:azure:storage:storageaccountscloud:azure:storage:storageaccounts:blobcloud:azure:storage:storageaccounts:filecloud:azure:storage:storageaccounts:queuecloud:azure:storage:storageaccounts:tablecloud:azure:storagesync:storagesyncservicescloud:azure:streamanalytics:streamingjobscloud:azure:synapse:workspacescloud:azure:synapse:workspaces:bigdatapoolscloud:azure:synapse:workspaces:sqlpoolscloud:azure:timeseriesinsights:environmentscloud:azure:timeseriesinsights:eventsourcescloud:azure:traffic_manager_profilecloud:azure:virtual_network_gatewaycloud:azure:web:appslotscloud:azure:web:functionslotscloud:azure:web:hostingenvironments:v2cloud:azure:web:serverfarmscloud:gcp:autoscalercloud:gcp:bigquery_biengine_modelcloud:gcp:cloud_functioncloud:gcp:cloud_run_revisioncloud:gcp:cloudsql_databasecloud:gcp:filestore_instancecloud:gcp:gae_appcloud:gcp:gce_instancecloud:gcp:gcs_bucketcloud:gcp:https_lbcloud:gcp:instance_groupcloud:gcp:internal_http_lb_rulecloud:gcp:internal_network_lb_rulecloud:gcp:k8s_clustercloud:gcp:k8s_containercloud:gcp:k8s_nodecloud:gcp:k8s_podcloud:gcp:network_lb_rulecloud:gcp:projectcloud:gcp:pubsub_snapshotcloud:gcp:pubsub_subscriptioncloud:gcp:pubsub_topiccloud:gcp:pubsublite_subscription_partitioncloud:gcp:pubsublite_topic_partitioncloud:gcp:tcp_ssl_proxy_rulecloud:gcp:tpu_workeros:service
Capabilities
Configure real-time updates
Currently, the Dynatrace API lacks support for programmatic webhook creation. To set up a webhook configuration in Dynatrace for sending alert notifications to the Ocean integration, follow these steps:
Prepare a webhook URL using this format: {app_host}/integration/webhook/problem.
The app_host parameter should match the ingress or external load balancer where the integration will be deployed.
For example, if your ingress or load balancer exposes the Dynatrace Ocean integration at https://myservice.domain.com,
your webhook URL should be https://myservice.domain.com/integration/webhook/problem.
- Go to Dynatrace.
- Go to Settings > Integration > Problem notifications.
- Select Add notification.
- Select Custom integration from the available notification types.
- Configure the notification using the following details.
Enabled- ensure the notification is enabled.Display name- use a meaningful name such as Port Ocean Webhook.Webhook URL- enter the value of theURLyou created above.- Enable Call webhook is new events merge into existing problems.
Custom payload- paste the following configuration:You can customize to your taste, the only important thing is the{
"State":"{State}",
"ProblemID":"{ProblemID}",
"ProblemTitle":"{ProblemTitle}"
}ProblemIDkey. The webhook integration will not work without it.Alerting profile- select the corresponding alerting profile.- Leave the rest of the fields as is.
- Click Save changes.
Examples
Examples of blueprints and the relevant integration configurations:
Entity
Entity blueprint
{
"identifier": "dynatraceEntity",
"description": "This blueprint represents a Dynatrace Entity",
"title": "Dynatrace Entity",
"icon": "Dynatrace",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"firstSeen": {
"type": "string",
"title": "First Seen",
"description": "The timestamp at which the entity was first seen, in UTC milliseconds.",
"format": "date-time"
},
"lastSeen": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Last Seen",
"description": "The timestamp at which the entity was last seen, in UTC milliseconds.",
"format": "date-time"
},
"type": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Type",
"description": "The type of the entity."
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Tags",
"description": "A list of tags of the entity.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Integration configuration
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: entity
selector:
query: "true"
entityTypes: ["APPLICATION", "SERVICE"] # An optional list of entity types to filter by. If not specified, defaults to ["APPLICATION", "SERVICE"].
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .entityId
title: .displayName
blueprint: '"dynatraceEntity"'
properties:
firstSeen: ".firstSeenTms / 1000 | todate"
lastSeen: ".lastSeenTms / 1000 | todate"
type: .type
tags: .tags[].stringRepresentation
Problem
Problem blueprint
{
"identifier": "dynatraceProblem",
"description": "This blueprint represents a Dynatrace Problem",
"title": "Dynatrace Problem",
"icon": "Dynatrace",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"entityTags": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Entity Tags",
"description": "A list of all entity tags of the problem.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"evidenceDetails": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Evidence Details",
"description": "A list of all evidence details of the problem.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"managementZones": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Management Zones",
"description": "A list of all management zones that the problem belongs to.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"problemFilters": {
"type": "array",
"title": "Problem Filters",
"description": "A list of alerting profiles that match the problem.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"severityLevel": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Severity Level",
"description": "The severity level of the problem.",
"enum": [
"AVAILABILITY",
"CUSTOM_ALERT",
"ERROR",
"INFO",
"MONITORING_UNAVAILABLE",
"PERFORMANCE",
"RESOURCE_CONTENTION"
],
"enumColors": {
"AVAILABILITY": "blue",
"CUSTOM_ALERT": "turquoise",
"ERROR": "red",
"INFO": "green",
"MONITORING_UNAVAILABLE": "darkGray",
"PERFORMANCE": "orange",
"RESOURCE_CONTENTION": "yellow"
}
},
"status": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Status",
"description": "The status of the problem.",
"enum": ["CLOSED", "OPEN"],
"enumColors": {
"CLOSED": "green",
"OPEN": "red"
}
},
"startTime": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Start Time",
"description": "The start time of the problem, in UTC milliseconds.",
"format": "date-time"
},
"endTime": {
"type": "string",
"title": "End Time",
"description": "The end time of the problem, in UTC milliseconds.",
"format": "date-time"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"impactedEntities": {
"title": "Impacted Entities",
"target": "dynatraceEntity",
"required": false,
"many": true
},
"linkedProblemInfo": {
"title": "Linked Problem Info",
"target": "dynatraceProblem",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"rootCauseEntity": {
"title": "Root Cause Entity",
"target": "dynatraceEntity",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
}
Integration configuration
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: problem
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .problemId
title: .title
blueprint: '"dynatraceProblem"'
properties:
entityTags: .entityTags[].stringRepresentation
evidenceDetails: .evidenceDetails.details[].displayName
managementZones: .managementZones[].name
problemFilters: .problemFilters[].name
severityLevel: .severityLevel
status: .status
startTime: ".startTime / 1000 | todate"
endTime: ".endTime | if . == -1 then null else (./1000 | todate) end"
relations:
impactedEntities: .impactedEntities[].entityId.id
linkedProblemInfo: .linkedProblemInfo.problemId
rootCauseEntity: .rootCauseEntity.entityId.id
SLO
SLO blueprint
{
"identifier": "dynatraceSlo",
"description": "This blueprint represents a Dynatrace SLO",
"title": "Dynatrace SLO",
"icon": "Dynatrace",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"status": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Status",
"description": "The status of the SLO.",
"enum": ["FAILURE", "WARNING", "SUCCESS"],
"enumColors": {
"FAILURE": "red",
"WARNING": "yellow",
"SUCCESS": "green"
}
},
"target": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Target",
"description": "The target value of the SLO."
},
"enabled": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Enabled",
"description": "Whether the SLO is enabled."
},
"warning": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Warning",
"description": "The warning value of the SLO. At warning state the SLO is still fulfilled but is getting close to failure."
},
"error": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Error",
"description": "The error of the SLO calculation. If the value differs from NONE, there is something wrong with the SLO calculation."
},
"errorBudget": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Error Budget",
"description": "The error budget of the calculated SLO."
},
"evaluatedPercentage": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Evaluated Percentage",
"description": "The calculated status value of the SLO."
},
"evaluationType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Evaluation Type",
"description": "The type of the SLO evaluation."
},
"filter": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Filter",
"description": "The filter for the SLO evaluation."
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Integration configuration
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: slo
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .id
title: .name
blueprint: '"dynatraceSlo"'
properties:
status: .status
target: .target
enabled: .enabled
warning: .warning
error: .error
errorBudget: .errorBudget
evaluatedPercentage: .evaluatedPercentage
evaluationType: .evaluationType
filter: .filter
Let's Test It
This section includes a sample response data from Dynatrace. In addition, it includes the entity created from the resync event based on the Ocean configuration provided in the previous section.
Payload
Here is an example of the payload structure from Dynatrace:
Entity response data
{
"displayName": "my host",
"entityId": "HOST-06F288EE2A930951",
"firstSeenTms": 1574697667547,
"fromRelationships": {
"isInstanceOf": [
{
"id": "HOST_GROUP-0E489369D663A4BF",
"type": "HOST_GROUP"
}
]
},
"icon": {
"customIconPath": "host",
"primaryIconType": "linux",
"secondaryIconType": "microsoft-azure-signet"
},
"lastSeenTms": 1588242361417,
"managementZones": [
{
"id": "6239538939987181652",
"name": "main app"
}
],
"properties": {
"bitness": 64,
"cpuCores": 8,
"monitoringMode": "FULL_STACK",
"networkZoneId": "aws.us.east01",
"osArchitecture": "X86",
"osType": "LINUX"
},
"tags": [
{
"context": "CONTEXTLESS",
"key": "architecture",
"stringRepresentation": "architecture:x86",
"value": "x86"
},
{
"context": "ENVIRONMENT",
"key": "Infrastructure",
"stringRepresentation": "[ENVIRONMENT]Infrastructure:Linux",
"value": "Linux"
}
],
"toRelationships": {
"isDiskOf": [
{
"id": "DISK-0393340DCA3853B0",
"type": "DISK"
}
]
},
"type": "HOST"
}
Problem response data
{
"affectedEntities": [
{
"entityId": {
"id": "string",
"type": "string"
},
"name": "string"
}
],
"displayId": "string",
"endTime": 1574697669865,
"entityTags": [
{
"context": "CONTEXTLESS",
"key": "architecture",
"stringRepresentation": "architecture:x86",
"value": "x86"
},
{
"context": "ENVIRONMENT",
"key": "Infrastructure",
"stringRepresentation": "[ENVIRONMENT]Infrastructure:Linux",
"value": "Linux"
}
],
"evidenceDetails": {
"details": [
{
"displayName": "Availability evidence",
"entity": {},
"evidenceType": "AVAILABILITY_EVIDENCE",
"groupingEntity": {},
"rootCauseRelevant": true,
"startTime": 1
},
{
"displayName": "User action evidence",
"entity": {},
"evidenceType": "USER_ACTION_EVIDENCE",
"groupingEntity": {},
"rootCauseRelevant": true,
"startTime": 1
}
],
"totalCount": 1
},
"impactAnalysis": {
"impacts": [
{
"estimatedAffectedUsers": 1,
"impactType": "APPLICATION",
"impactedEntity": {}
}
]
},
"impactLevel": "APPLICATION",
"impactedEntities": [{}],
"linkedProblemInfo": {
"displayId": "string",
"problemId": "string"
},
"managementZones": [
{
"id": "string",
"name": "HOST"
}
],
"problemFilters": [
{
"id": "E2A930951",
"name": "BASELINE"
}
],
"problemId": "06F288EE2A930951",
"recentComments": {
"comments": [
{
"authorName": "string",
"content": "string",
"context": "string",
"createdAtTimestamp": 1,
"id": "string"
}
],
"nextPageKey": "AQAAABQBAAAABQ==",
"pageSize": 1,
"totalCount": 1
},
"rootCauseEntity": {},
"severityLevel": "AVAILABILITY",
"startTime": 1574697667547,
"status": "CLOSED",
"title": "title"
}
SLO response data
{
"burnRateMetricKey": "func:slo.errorBudgetBurnRate.payment_service_availability",
"denominatorValue": 90,
"description": "Rate of successful payments per week",
"enabled": true,
"error": "NONE",
"errorBudget": 1.25,
"errorBudgetBurnRate": {
"burnRateType": "SLOW",
"burnRateValue": 1.25,
"burnRateVisualizationEnabled": true,
"estimatedTimeToConsumeErrorBudget": 24,
"fastBurnThreshold": 1.5,
"sloValue": 95
},
"errorBudgetMetricKey": "func:slo.errorBudget.payment_service_availability",
"evaluatedPercentage": 96.25,
"evaluationType": "AGGREGATE",
"filter": "type(\"SERVICE\")",
"id": "123e4567-e89b-42d3-a456-556642440000",
"metricDenominator": "builtin:service.requestCount.server",
"metricExpression": "(100)*(builtin:service.errors.server.successCount:splitBy())/(builtin:service.requestCount.server:splitBy())",
"metricKey": "func:slo.payment_service_availability",
"metricNumerator": "builtin:service.errors.server.successCount",
"metricRate": "builtin:service.successes.server.rate",
"name": "Payment service availability",
"normalizedErrorBudgetMetricKey": "func:slo.normalizedErrorBudget.payment_service_availability",
"numeratorValue": 80,
"problemFilters": "[type(\"SERVICE\")]",
"relatedOpenProblems": 1,
"relatedTotalProblems": 1,
"status": "WARNING",
"target": 95,
"timeframe": "-1d",
"useRateMetric": true,
"warning": 97.5
}
Mapping Result
The combination of the sample payload and the Ocean configuration generates the following Port entity:
Entity entity in Port
{
"identifier": "HOST-06F288EE2A930951",
"title": "my host",
"blueprint": "dynatraceEntity",
"team": [],
"icon": "Dynatrace",
"properties": {
"firstSeen": "2019-11-25T14:14:27Z",
"lastSeen": "2020-04-30T14:52:41Z",
"type": "HOST",
"tags": ["architecture:x86", "[ENVIRONMENT]Infrastructure:Linux"]
},
"relations": {},
"createdAt": "2024-2-6T09:30:57.924Z",
"createdBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW",
"updatedAt": "2024-2-6T11:49:20.881Z",
"updatedBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW"
}
Problem entity in Port
{
"identifier": "06F288EE2A930951",
"title": "title",
"blueprint": "dynatraceProblem",
"team": [],
"icon": "Dynatrace",
"properties": {
"entityTags": ["architecture:x86", "[ENVIRONMENT]Infrastructure:Linux"],
"evidenceDetails": ["Availability evidence", "User action evidence"],
"managementZones": ["HOST"],
"problemFilters": ["BASELINE"],
"severityLevel": "AVAILABILITY",
"status": "CLOSED",
"startTime": "2019-11-25T14:14:27Z",
"endTime": "2020-04-30T14:52:41Z"
},
"relations": {
"impactedEntities": ["HOST-06F288EE2A930951"],
"linkedProblemInfo": "06F288EE2A930951",
"rootCauseEntity": "HOST-06F288EE2A930951"
},
"createdAt": "2024-2-6T09:30:57.924Z",
"createdBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW",
"updatedAt": "2024-2-6T11:49:20.881Z",
"updatedBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW"
}
SLO entity in Port
{
"identifier": "123e4567-e89b-42d3-a456-556642440000",
"title": "Payment service availability",
"blueprint": "dynatraceSlo",
"team": [],
"icon": "Dynatrace",
"properties": {
"status": "WARNING",
"target": 95,
"enabled": true,
"warning": 97.5,
"error": "NONE",
"errorBudget": 1.25,
"evaluatedPercentage": 96.25,
"evaluationType": "AGGREGATE",
"filter": "type(\"SERVICE\")"
},
}
Alternative installation via webhook
While the Ocean integration described above is the recommended installation method, you may prefer to use a webhook to ingest problem from Dynatrace. If so, use the following instructions:
Note that when using this method, data will be ingested into Port only when the webhook is triggered.
Webhook installation (click to expand)
Port configuration
Create the following blueprint definitions:
Dynatrace microservice blueprint
{
"identifier": "microservice",
"title": "Microservice",
"icon": "Service",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"title": "Description",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Dynatrace problem blueprint
{
"identifier": "dynatraceProblem",
"description": "This blueprint represents a Dynatrace problem in our software catalog",
"title": "Dynatrace Problem",
"icon": "Deployment",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"state": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Problem State"
},
"url": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Problem URL"
},
"details": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Details"
},
"impact": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Problem Impact"
},
"severity": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Problem Severity"
},
"tags": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Tags"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"microservice": {
"title": "Impacted Services",
"target": "microservice",
"required": false,
"many": true
}
}
}
Create the following webhook configuration using Port's UI:
Dynatrace problem webhook configuration
-
Basic details tab - fill the following details:
- Title :
Dynatrace Problem Mapper; - Identifier :
dynatrace_problem_mapper; - Description :
A webhook configuration for problem events from Dynatrace; - Icon :
Dynatrace;
- Title :
-
Integration configuration tab - fill the following JQ mapping:
[
{
"blueprint": "dynatraceProblem",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.PID | tostring",
"title": ".body.ProblemTitle",
"properties": {
"state": ".body.State",
"url": ".body.ProblemURL",
"details": ".body.ProblemDetailsText",
"impact": ".body.ProblemImpact",
"severity": ".body.ProblemSeverity",
"tags": ".body.ProblemTags | split(\", \")"
},
"relations": {
"microservice": "[.body.ImpactedEntities[].entity]"
}
}
}
] -
Click Save at the bottom of the page.
The webhook configuration's relation mapping will function properly only when the identifiers of the Port microservice entities match the names of the entities in your Dynatrace.
If there is a mismatch, you can utilize Dynatrace Tags to align the actual identifier in Port.
To do this, create a tag with the key proj and value microservice_identifier.
Then, update the relation JQ syntax to establish a connection between the Dynatrace problem and the Port microservice. Here is the updated JQ Mappings:
{
"blueprint": "dynatraceProblem",
"entity": {
...Properties mappings,
"relations": {
"microservice": ".body.ProblemTags | split(\", \") | map(select(test(\"proj:\")) | sub(\"proj:\";\"\"))"
}
}
}
Details
JQ expression explained
The above JQ expression will split the tags by comma and space, then filter the tags that start withproj: and remove the proj: prefix from the tag value.Create a webhook in Dynatrace
- Log in to Dynatrace with your credentials.
- Click on Settings at the left sidebar of the page.
- Choose Integration and click on Problem notifications.
- Select Add notification.
- Select Custom integration from the available integration types.
- Input the following details:
-
Display name- use a meaningful name such as Port Webhook. -
Webhook URL- enter the value of theurlkey you received after creating the webhook configuration. -
Overview- you can add an optional HTTP header to your webhook request. -
Custom payload- When a problem is detected or resolved on your entity, this payload will be sent to the webhook URL. You can enter this JSON placeholder in the textbox:{
"State":"{State}",
"PID":"{PID}",
"ProblemTitle":"{ProblemTitle}",
"ImpactedEntity": "{ImpactedEntity}",
"ProblemDetailsText": "{ProblemDetailsText}",
"ProblemImpact": "{ProblemImpact}",
"ProblemSeverity": "{ProblemSeverity}",
"ProblemURL": "{ProblemURL}",
"ProblemTags": "{ProblemTags}",
"ImpactedEntities": {ImpactedEntities}
} -
Alerting profile- configure your preferred alerting rule or use the default one.
-
- Click Save changes at the bottom of the page.
To view the different payloads and events available in Dynatrace webhooks, look here.
Done! Any problem detected on your Dynatrace entity will trigger a webhook event. Port will parse the events according to the mapping and update the catalog entities accordingly.
Let's Test It
This section includes a sample response data from Dynatrace. In addition, it includes the entity created from the resync event based on the Ocean configuration provided in the previous section.
Payload
Here is an example of the payload structure from Dynatrace:
Problem response data
{
"affectedEntities": [
{
"entityId": {
"id": "string",
"type": "string"
},
"name": "string"
}
],
"displayId": "string",
"endTime": 1574697669865,
"entityTags": [
{
"context": "CONTEXTLESS",
"key": "architecture",
"stringRepresentation": "architecture:x86",
"value": "x86"
},
{
"context": "ENVIRONMENT",
"key": "Infrastructure",
"stringRepresentation": "[ENVIRONMENT]Infrastructure:Linux",
"value": "Linux"
}
],
"evidenceDetails": {
"details": [
{
"displayName": "Availability evidence",
"entity": {},
"evidenceType": "AVAILABILITY_EVIDENCE",
"groupingEntity": {},
"rootCauseRelevant": true,
"startTime": 1
},
{
"displayName": "User action evidence",
"entity": {},
"evidenceType": "USER_ACTION_EVIDENCE",
"groupingEntity": {},
"rootCauseRelevant": true,
"startTime": 1
}
],
"totalCount": 1
},
"impactAnalysis": {
"impacts": [
{
"estimatedAffectedUsers": 1,
"impactType": "APPLICATION",
"impactedEntity": {}
}
]
},
"impactLevel": "APPLICATION",
"impactedEntities": [{}],
"linkedProblemInfo": {
"displayId": "string",
"problemId": "string"
},
"managementZones": [
{
"id": "string",
"name": "HOST"
}
],
"problemFilters": [
{
"id": "E2A930951",
"name": "BASELINE"
}
],
"problemId": "06F288EE2A930951",
"recentComments": {
"comments": [
{
"authorName": "string",
"content": "string",
"context": "string",
"createdAtTimestamp": 1,
"id": "string"
}
],
"nextPageKey": "AQAAABQBAAAABQ==",
"pageSize": 1,
"totalCount": 1
},
"rootCauseEntity": {},
"severityLevel": "AVAILABILITY",
"startTime": 1574697667547,
"status": "CLOSED",
"title": "title"
}
Mapping Result
The combination of the sample payload and the Ocean configuration generates the following Port entity:
Problem entity in Port
{
"identifier": "06F288EE2A930951",
"title": "title",
"blueprint": "dynatraceProblem",
"team": [],
"icon": "Dynatrace",
"properties": {
"entityTags": ["architecture:x86", "[ENVIRONMENT]Infrastructure:Linux"],
"evidenceDetails": ["Availability evidence", "User action evidence"],
"managementZones": ["HOST"],
"problemFilters": ["BASELINE"],
"severityLevel": "AVAILABILITY",
"status": "CLOSED",
"startTime": "2019-11-25T14:14:27Z",
"endTime": "2020-04-30T14:52:41Z"
},
"relations": {
"impactedEntities": ["HOST-06F288EE2A930951"],
"linkedProblemInfo": "06F288EE2A930951",
"rootCauseEntity": "HOST-06F288EE2A930951"
},
"createdAt": "2024-2-6T09:30:57.924Z",
"createdBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW",
"updatedAt": "2024-2-6T11:49:20.881Z",
"updatedBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW"
}
Ingest Dynatrace Entities
In this example,
you will create a dynatrace_entity blueprint that ingests monitored entities from your Dynatrace account.
You will then add a Python script to make API calls to Dynatrace REST API and fetch data for your account.